Back
"Dwell fatigue" is a phenomenon that can occur in titanium alloys when held under stress, such as a jet engine's fan disc during takeoff. This peculiar failure mode can initiate microscopic cracks that drastically reduce a component's lifetime. The most widely used titanium alloy, Ti-6Al-4V, was not believed to exhibit dwell fatigue before the 2017 Air France Flight 066…
The Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM) and Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) announced that they have awarded the 2023 SIAM/ACM Prize in Computational Science and Engineering to the team behind the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL)-developed SUNDIALS software suite. The prestigious award is handed out every two years and recognizes…
The High-Performance Computing for Energy Innovation (HPC4EI) initiative has opened its fall 2022 solicitation cycle to industry partners interested in collaborating with the Department of Energy (DOE) to address key energy and decarbonization-related challenges. The sponsors of this solicitation are the HPC4Manufacturing (HPC4Mfg) and HPC4Materials (HPC4Mtls) programs,…
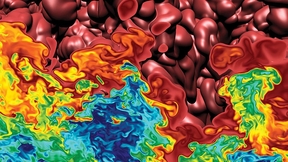
Two Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory-led teams received SciVis Test of Time awards at the 2022 IEEE VIS conference on Oct. 18, for papers that have achieved lasting relevancy in the field of scientific visualization. Published in 2008, an LLNL-led paper that — for the first time — allowed Digital Morse Theory to be applied to large scale and three-dimensional data,…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers are starting work on a three-year project aimed at improving methods for visual analysis of large heterogeneous data sets as part of a recent Department of Energy funding opportunity. The joint project, titled “Neural Field Processing for Visual Analysis,” will be led at LLNL by co-principal investigator (PI) Andrew…
While Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is eagerly awaiting the arrival of its first exascale-class supercomputer, El Capitan, physicists and computer scientists running scientific applications on testbeds for the machine are getting a taste of what to expect. “I'm not exactly sure we’ve wrapped our head around exactly about how much compute power [El Capitan] is…
A high performance computing (HPC) project led by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers was one of 22 recently awarded funding by the Department of Energy (DOE) under the 2022 “Exploratory Research for Extreme-Scale Science” (EXPRESS) program. LLNL computational mathematician Tzanio Kolev will serve as principal investigator on the project, which includes LLNL…
The last nuclear test, code-named Divider, took place 30 years ago, on Sept. 23, 1992. That year, President Bush declared a temporary moratorium on nuclear testing, which became permanent during the Clinton administration. This ending of the era of nuclear testing was also the beginning of stockpile stewardship. Leaders from the Department of Energy (DOE), and Lawrence…
Scientific discovery during the Stockpile Stewardship Program maintains confidence in the nuclear deterrent without testing, brings other benefits The last nuclear test, code-named Divider, took place 30 years ago, on September 23, 1992. That year, President Bush declared a temporary moratorium on nuclear testing, which became permanent during the Clinton administration…
The last nuclear test, code-named Divider, took place 30 years ago, on Sept. 23, 1992. That year, President Bush declared a temporary moratorium on nuclear testing, which became permanent in 1995, during the Clinton administration. This ending of the era of nuclear testing coincided with a Presidential announcement of the beginning of stockpile stewardship. As the decision…
NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) spacecraft will crash into asteroid Dimorphos on Sept. 26, executing the first asteroid deflection test that has been years in the planning. Dimorphos, at 150 meters across, is the “moonlet” of a binary asteroid system, orbiting the larger companion asteroid, Didymos (800 meters). The momentum of the ~600 kg spacecraft,…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and engineers have garnered three awards among the top 100 industrial inventions worldwide. The trade journal R&D World Magazine recently announced the winners of the awards, often called the “Oscars of invention,” recognizing new commercial products, technologies and materials that are available for sale or…
The High Performance Computing for Energy Innovation (HPC4EI) initiative will hold a special webinar on Oct. 7 to celebrate Manufacturing Day and provide a forum for industry experts and Department of Energy (DOE) scientists to discuss how HPC can help combat climate change and improve energy efficiency. The virtual event begins at 8 a.m. PDT and brings together panelists…
The leaders of Case Western Reserve University and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) to accelerate their efforts in shared areas of excellence. After three years of growing institutional collaboration in such areas as energy, materials science and polymer processing, Case Western Reserve President Eric W. Kaler…
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team claimed a top prize at an inaugural international symbolic regression competition for an artificial intelligence (AI) framework they developed capable of explaining and interpreting real-life COVID-19 data. Hosted by the open source SRBench project at the 2022 Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference (GECCO), the…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) has signed a memorandum of understanding with high performance computing (HPC) facilities in Germany, the United Kingdom and the United States, jointly forming the International Association of Supercomputing Centers (IASC). LLNL and co-founders — the Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC) Hartree Centre, the National…
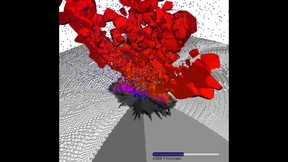
The IEEE Nuclear and Plasma Sciences Society (NPSS) announced a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team as the winner of its 2022 Transactions on Plasma Science (TPS) Best Paper Award for their work applying machine learning to inertial confinement fusion (ICF) experiments. In the paper, lead author Kelli Humbird and co-authors propose a novel technique for…
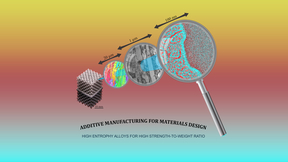
Metal 3D printing is used to produce components for many commercial applications, particularly in the transportation sector, where printing methods such as laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF) can produce super-strong and ultralight complex-shaped components that cannot be manufactured with conventional techniques. But while laser-based methods enable the manufacturing of…
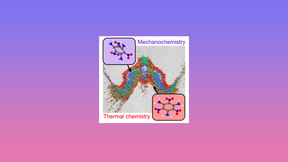
Scientists at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) Energetic Materials Center and Purdue University Materials Engineering Department used simulations performed on the LLNL supercomputer Quartz to uncover a general mechanism that accelerates chemistry in detonating explosives critical to managing the nation’s nuclear stockpile. Their research is featured in the…
Recent advances in pre-programmed architected materials could enable new functions that can evolve in response to their environments or external stimuli, according to Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers. In a paper published by Nature Reviews Materials, LLNL researchers provide an overview of the progress made in responsive architected materials that…