Back
Editor’s note: The principal mission of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL)’s National Ignition Facility (NIF) is to support the National Nuclear Security Administration’s science-based Stockpile Stewardship Program — and with the achievement of fusion ignition in 2022 at NIF, LLNL is further exploring the possible use of nuclear fusion as a future energy source…
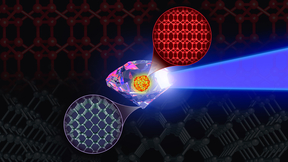
Diamond is the strongest material known. However, another form of carbon has been predicted to be even tougher than diamond. The challenge is how to create it on Earth. The eight-atom body-centered cubic (BC8) crystal is a distinct carbon phase: not diamond, but very similar. BC8 is predicted to be a stronger material, exhibiting a 30% greater resistance to compression…
A new satellite called XRISM (X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission, pronounced “crism”) was successfully launched from the Tanegashima Space Center in Japan on Sep. 7, 2023. XRISM is a collaboration between the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), with European Space Agency participation, to study extreme…
Advances in astronomical observations have resulted in the discovery of an extraordinary number of extrasolar planets, some of which are believed to have a rocky composition similar to Earth. Learning more about their interior structure could provide important clues about their potential habitability. Led by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), a team of…
High performance computing (HPC) simulations exploring star formation by Lawrence Livermore astrophysicist Richard Klein were among select research highlights featured by NASA at the recent supercomputing conference in Austin, Texas.Klein’s "Simulating Star Formation: From Giant Molecular Clouds to Protostellar Clusters" presentation is now on NASA’s website.The origin of…
Determining the chemical abundance pattern left by the earliest stars in the universe is no easy feat. A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientist is helping to do just that.The first stars in the universe formed about 400 million years after the Big Bang (estimated at 13.8 billion years ago). Inside of these stellar furnaces, nuclear processes fused the…
Multilayer-coated mirrors, if used as focusing optics in the soft gamma-ray photon energy range, can enable and advance a range of scientific and technological applications that would benefit from the large improvements in sensitivity and resolution that true imaging provides. In a paper published in a recent online edition of Optics Express, LLNL postdoc Nicolai Brejnholt…
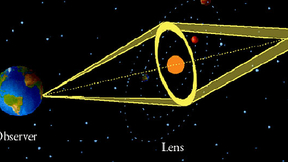
LIVERMORE, Calif. --There are more exoplanets further away from their parent stars than originally thought, according to new astrophysics research. In a new paper appearing in the Jan. 12 edition of the journal, Nature , astrophysicist Kem Cook as part of an international collaboration, analyzed microlensing data that bridges the gap between a recent finding of planets…