Back
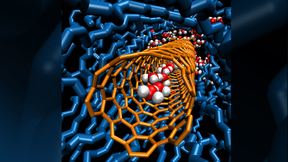
Lawrence Livermore (LLNL) scientists, in collaboration with researchers at Northeastern University, have developed carbon nanotube pores that can exclude salt from seawater. The team also found that water permeability in carbon nanotubes (CNTs) with diameters smaller than a nanometer (0.8 nm) exceeds that of wider carbon nanotubes by an order of magnitude. The nanotubes,…
Just as members of a marching band align themselves for a performance, carbon nanotubes create a similar configuration. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists recently used synchrotron X-ray scattering to fully capture the hierarchical structure in self-organized carbon nanotube materials from the atomic to micrometer scale. Their work, recently published…
For the first time, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory scientists and collaborators have captured a movie of how large populations of carbon nanotubes grow and align themselves.Understanding how carbon nanotubes (CNT) nucleate, grow and self-organize to form macroscale materials is critical for application-oriented design of next-generation supercapacitors, electronic…
Members of the LLNL team that created an environmentally reactive "second skin" for use in military uniforms of the future will be answering questions from the public during a Reddit "Ask Me Anything" online event beginning at 10 a.m. Wednesday. In addition to addressing just about any question on the minds of the Reddit community, Lab scientists Francesco Fornasiero, Ngo…
In work that aims to protect soldiers from biological and chemical threats, a team of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory scientists has created a material that is highly breathable yet protective from biological agents. This material is the first key component of futuristic smart uniforms that also will respond to and protect from environmental chemical hazards. The…
For the first time, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have shown that carbon nanotubes as small as eight-tenths of a nanometer in diameter can transport protons faster than bulk water, by an order of magnitude.The research validates a 200-year old mechanism of proton transport.A nanometer is one billionth of a meter. By comparison, the diameter of a…
Lawrence Livermore scientists have found that carbon nanotubes can help with tissue healing and repair.The team, which includes scientists from The Feinstein Institute for Medical Research, UC Davis and UC Merced, found that there is long-term biocompatibility of single wall carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) when used for tissue engineering and articular cartilage.Carbon nanotubes…
LIVERMORE, Calif. - Researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) in Zurich have developed a new method of using nanotubes to detect molecules at extremely low concentrations enabling trace detection of biological threats, explosives and drugs. The joint research team, led by LLNL Engineer Tiziana Bond…
Researchers in carbon nanotubes, originally developed at the Laboratory, have been awarded more than $100,000 by the California Energy Commission to apply the technology to curbing industrial pollution. Hayward-based Porifera, Inc., headed by former Lab scientist Olgica Bakajin, was awarded $115,397 for a project to research and develop carbon nanotube membranes to…