Back
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL) Pandora SmallSat mission recently passed NASA’s critical design review: a major milestone for the mission to continue its journey toward launch. The Pandora SmallSat mission will study planets beyond our solar system, known as exoplanets, and their stars. “This is a major milestone for the mission and a huge accomplishment…
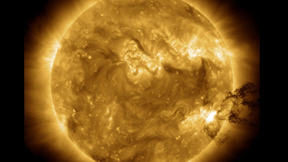
On Monday, April 8, a swath of North America will experience a total solar eclipse. For a few minutes, the moon will completely obscure the sun and viewers will be able to see the intricate loops and flares in the solar corona—normally washed out by the bright disk of the sun. In the corona, the outermost, gaseous part of the sun’s atmosphere, particles dance around…
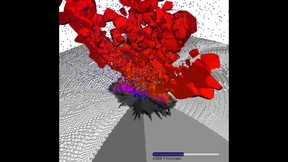
Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have developed a modeling tool for assessing the potential use of a nuclear device to defend the planet against catastrophic asteroid impacts. The research, published today in the Planetary Science Journal, introduces a novel approach to simulating the energy deposition from a nuclear device on an asteroid's…
A new satellite called XRISM (X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission, pronounced “crism”) was successfully launched from the Tanegashima Space Center in Japan on Sep. 7, 2023. XRISM is a collaboration between the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), with European Space Agency participation, to study extreme…
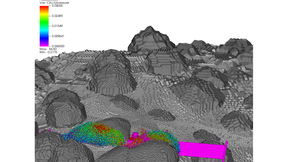
An instrument designed and built by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers departed Earth last week on a two-billion-mile, nearly six-year journey through space to explore a rare, largely metal asteroid. The Livermore high-purity germanium (HPGe) gamma-ray sensor is an essential part of a larger gamma-ray spectrometer (GRS) built in collaboration with…
Every year, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) welcomes hundreds of interns for an experiential, hands-on approach to learning. Working with some of the brightest minds in their fields, LLNL’s interns have the opportunity to explore new projects, build their skills, connect with mentors and integrate into Lab culture — resulting in a meaningful experience that…
When SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft docked with the International Space Station (ISS) on March 16, it delivered several thousand pounds of supplies for the crew as well as new hardware. The hardware included the U.S. Space Force’s Space Test Program Houston 9 (STP-H9) platform, which houses a prototype telescope designed and built by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's…
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) engineer and the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory are among those sharing a Department of Energy (DOE) award for their roles in building the world’s newest observatory. The DOE honor, the 2021 project management achievement award, was recently presented for work done on the Legacy Survey of Space and Time camera (LSSTCam)…
Planetary defense physicist Megan Bruck Syal on Wednesday represented Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) at “Space STEM Task Force Pathways to the Federal Space Workforce,” an outreach event hosted by the National Science Foundation. Multiple federal government agencies came together in a virtual interactive session to provide information for students, early…
A prototype telescope designed and built by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers has been launched from Cape Canaveral, Fla., to the International Space Station (ISS). Known as the Stellar Occultation Hypertemporal Imaging Payload (SOHIP), the telescope uses LLNL patented-monolithic optics technology on a gimbal to observe and measure atmospheric…
On the morning of Feb. 15, 2013, a small asteroid exploded over Chelyabinsk, Russia, sending a loud shockwave and sonic boom across the region, damaging buildings and leaving around 1,200 people injured. The resulting meteor, with a diameter of approximate 20 meters (roughly the size of a six-story building), was one of the largest to be detected breaking up in the Earth’s…
The first peer-reviewed results from NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission were published Wednesday by Nature, including contributions from LLNL’s planetary defense team. The DART spacecraft executed a successful hypervelocity impact of 150-meter asteroid Dimorphos on Sept. 26, 2022. Analysis by Earth-based telescopes determined that the impact…
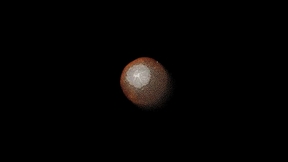
Samples from asteroid Ryugu returned by the Hayabusa2 mission contain evidence of extensive alteration by water and appear related to CI chondrites, which are believed to best represent the bulk of the solar system composition. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists in collaboration with an international team looked at the isotopic composition of oxygen,…
California native Kerianne Pruett started at LLNL in 2019 as an intern, and now works as a spacecraft systems engineer, matrixed to the Physics Division. At the Laboratory, Pruett utilizes data science, machine learning, and high-performance computing to answer questions about dark matter, dark energy, and space domain awareness.
Today at 4:14 p.m. (PDT), NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) Mission will execute the first-ever asteroid-deflection test by crashing into asteroid Dimorphos. Traveling at ~6 km/s with a mass of ~600 kg, the DART spacecraft will transfer enough momentum for the imparted change in velocity to be detectable from Earth-based telescopes. However, there is…
NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) spacecraft will crash into asteroid Dimorphos on Sept. 26, executing the first asteroid deflection test that has been years in the planning. Dimorphos, at 150 meters across, is the “moonlet” of a binary asteroid system, orbiting the larger companion asteroid, Didymos (800 meters). The momentum of the ~600 kg spacecraft,…
No need to worry, it is just a very small piece for scientific study. In December 2014, the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency launched the spacecraft Hayabusa2 to the asteroid 162173 Ryugu. In December 2020, when the sample-return capsule successfully landed safely back on Earth with pristine pieces of Ryugu that it had collected, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory…
Last month, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), a partnership with the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency, revealed unprecedented and detailed views of the universe, with the release of its first full-color images and spectroscopic data. The cosmic objects that Webb targeted for these first observations were released July 12 and are available on the…
Collaborative research and development focused on the extreme ultraviolet (EUV) end of the spectrum has resulted in state-of-the-art, multilayer reflective optics used for space exploration, manufacturing microchips, and more.
Earth’s supply of water is incredibly important for its ability to sustain life, but where did that water come from? Was it present when Earth formed or was it delivered later by meteorites or comets from outer space? The source of Earth’s water has been a longstanding debate and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists think they have the answer — and they…