Back
Getting the chance to meet and mingle with scientists who have achieved Nobel Prize winning greatness will be the reality for five Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) postdoctoral appointees selected to attend the 73rd annual Lindau Nobel Laureate meetings. Tina Ebert, Elizabeth Grace and Raspberry Simpson were selected as the 2024 LLNL cohort; Tomi Akindele and…
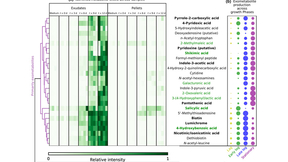
Microalgae play important roles in global carbon cycling and industrial applications for bioproduct and biofuel production. As with land plants and other host–microbial systems, microalgal activity, productivity, and stability are closely tied to surrounding microbial communities. However, a predictive understanding of microbial community interactions with algae is still…
Particulate soil carbon may be more vulnerable to microbial decomposition under warmer temperatures associated with climate change. Soil organic matter contains more carbon than plants and the atmosphere combined. Soil is increasingly considered for its potential role in climate mitigation due to its ability to sequester more carbon, but it also is critical to understand…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) employees, participating in five project teams, recently earned Department of Energy (DOE) Secretary’s Honor Awards. In addition, Karin King of the Livermore Field Office was honored for her role in the Leadership in Climate Action Team. Representing some of the highest internal, non-monetary recognition that DOE employees and…
TATB (1,3,5-triamino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene) is an important explosive compound because of its extensive use in munitions and world-wide weapons systems. Despite its importance, researchers have been trying to understand its response to temperature extremes for the past 50 years. A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team has uncovered a new thermal decomposition…
Six scientists at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) were recently granted awards through the Lab’s 2023 Academic Collaboration Team (ACT) annual call for proposals. Awards support university research partners for up to three years to perform research in collaboration with Lab scientists and offer an important way to build long-term connections with…
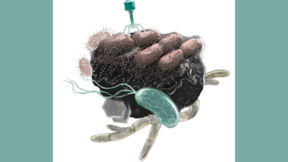
Ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms (AOM) use ammonia for energy and account for the annual oxidation of approximately 2.3 trillion kilograms of nitrogen in soil, freshwater, the subsurface and man-made ecosystems. But one major question that has remained unanswered for decades is how different AOM species coexist in the same environment: do they compete for ammonia or…
Microbes are major drivers of carbon and nutrient fluxes in Earth’s terrestrial ecosystems; however, Earth system models used for climate change adaptation and mitigation strategies typically exclude explicit representation of soil microorganisms. A team of researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBL) and…
The development of new antibiotics has stalled — new strategies are needed as the world enters the age of antibiotic resistance. To combat this challenge, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists have found that synthetic antibacterial minerals exhibit potent antibacterial activity against topical MRSA infections and increase the rate of wound closure…
Soil is a highly complex microbial habitat that is home to tens of millions of microbial populations, where biotic and abiotic factors shape microbial community structure. Moments of acute pressure on a community, such as rapid environmental changes or fluxes in resource availability, drive successional trajectories that result in altered community structures. One such…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers, along with scientists from more than a dozen institutions, have completed a first-of-its-kind high-resolution assessment of carbon dioxide (CO2) removal (CDR) in the United States. The report, “Roads to Removal: Options for Carbon Dioxide Removal in the United States,” charts a path for the United States to achieve…
Past and present nuclear activities (energy, research and weapon tests) have increased the need to understand the behavior of radioactive materials in the environment. Nuclear wastes containing actinides (such as plutonium, americium, curium and neptunium) are particularly problematic as they remain radioactive and toxic for thousands of years. However, when compared to…
While neutrinos are one of the most common particles in the universe, their elusive nature makes it challenging to understand their behavior. In new research from the Precision Reactor Oscillation and Spectrum (PROSPECT) Experiment, scientists have produced final results from measurements of neutrinos emitted by a nuclear reactor at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Their…
Beneath the Earth's surface, a relentless conflict unfolds as soil viruses prey on their tiny microbial hosts, fundamentally shaping our planet's ecosystems. New research from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and their collaborators at the University of California, Berkeley illuminates a fascinating phenomenon: the demise of soil bacteria and other…
The groundbreaking discoveries and scientific advancements that take place at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and across the broader national laboratory system rely on the passage of information from tenured staff scientists to new interns and early career scientists. This past summer, Zachary (Zach) Murphy, a Ph.D. student studying chemistry at the…
An instrument designed and built by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers departed Earth last week on a two-billion-mile, nearly six-year journey through space to explore a rare, largely metal asteroid. The Livermore high-purity germanium (HPGe) gamma-ray sensor is an essential part of a larger gamma-ray spectrometer (GRS) built in collaboration with…
Miguel Cisneros is a first-generation Mexican American whose journey in life has taken him to explore and navigate the unknown fearlessly. Growing up, Cisneros was an only child who welcomed new adventures. His interest in exploring new experiences and places is something he continues to do to this day. Cisneros’ parents migrated from Mexico to the United States for a…
Two graduate students have earned Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science Graduate Student Research (SCGSR) Program awards to perform their doctoral dissertation research at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). The prestigious award helps cover living expenses and travel for 60 students from universities across the nation. Their proposed research projects…
Neutron-capture reactions on unstable nuclei play a key role in the production of heavy elements in the universe and provide vital diagnostics for reaction networks related to stockpile stewardship. However, these reactions cannot be measured directly because they involve radioactive nuclei. Lawrence Livermore researchers have performed indirect measurements to constrain…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists will lead and co-lead projects in support of the Department of Energy’s (DOE) new Energy Earthshot program. The Energy Earthshots Initiative calls for innovation and collaboration to tackle the toughest topics in energy-related research. In January, DOE announced Office of Science funding for the Energy Earthshot…