Back
The High Performance Computing for Energy Innovation (HPC4EI) Program, managed by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) for the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), is seeking new industry proposals for short-term projects that could benefit from world-class DOE high performance computing (HPC) and expertise. Under the fall 2020 HPC4EI solicitation, DOE’s Office of…
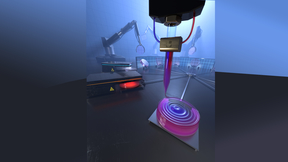
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have used multi-material 3D printing to create tailored gradient refractive index glass optics that could make for better military specialized eyewear and virtual reality goggles. The new technique could achieve a variety of conventional and unconventional optical functions in a flat glass component (with no surface…
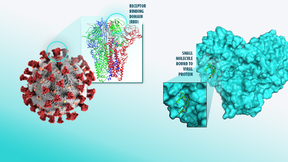
A machine learning model developed by a team of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists to aid in COVID-19 drug discovery efforts is a finalist for the Gordon Bell Special Prize for High Performance Computing-Based COVID-19 Research. Using Sierra, the world’s third fastest supercomputer, LLNL scientists created a more accurate and efficient generative…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) can lay claim to housing four of the world’s 100 most powerful supercomputers, more than any other institution according to the TOP500 List announced Monday during the virtual Supercomputing 2020 conference (SC20). The 125-petaFLOP peak Sierra, the National Nuclear Security Administration’s flagship supercomputer, remained…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) can lay claim to housing four of the world’s 100 most powerful supercomputers, more than any other institution according to the TOP500 List announced Monday during the virtual Supercomputing 2020 conference (SC20). The 125-petaFLOP peak Sierra, the National Nuclear Security Administration’s flagship supercomputer, remained…
With funding from the Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security (CARES) Act, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), chipmaker AMD and information technology company Supermicro have upgraded the supercomputing cluster Corona, providing additional resources to scientists for COVID-19 drug discovery and vaccine research. The recent addition of nearly 1,000 AMD…
The Department of Energy (DOE) today announced two rounds of awards for the High Performance Computing for Energy Innovation Program (HPC4EI), including five projects at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). HPC4EI connects industry with the computational resources and expertise of the DOE national laboratories to solve challenges in manufacturing, accelerate…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), along with partners Intel, Supermicro and Cornelis Networks, have deployed “Ruby,” a high performance computing (HPC) cluster that will perform functions for the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) and support the Laboratory’s COVID-19 research. Funded by NNSA’s Advanced Simulation and Computing (ASC) program, the…
After more than two years of joint research, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), Total and Stanford University are releasing an open-source, high-performance simulator for large-scale geological carbon dioxide (CO2) storage. The GEOSX simulator will enable researchers around the world to build on the work of the three partners, providing an open framework to…
The scientific computing and networking leadership of 17 Department of Energy (DOE) national laboratories will be showcased at SC20, the International Conference for High-Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, taking place Nov. 9-19 for the first time via a completely virtual format. Like most conferences and workshops being held this year across the U.S…
The Association for Women in Mathematics (AWM) announced it has named Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) computational scientist Carol Woodward as a 2021 fellow, recognizing her commitment to supporting and advancing women in the mathematical sciences. A computational mathematician in the Center for Applied Scientific Computing (CASC) since 1996, Woodward’s…
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team has simulated the cross-linking of 3D-printed polymer networks, a key step toward developing new functional resins for light-based 3D-printing techniques including two-photon lithography (TPL) and volumetric additive manufacturing (VAM). The team used molecular dynamics simulations to study, at a microscopic level, the…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and its partners AMD, Supermicro and Cornelis Networks have installed a new high performance computing (HPC) cluster with memory and data storage capabilities optimized for data-intensive COVID-19 research and pandemic response. Funded by the Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security (CARES) Act, the “big memory” cluster,…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) has installed a state-of-the-art artificial intelligence (AI) accelerator from SambaNova Systems, the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) announced today, allowing researchers to more effectively combine AI and machine learning (ML) with complex scientific workloads. LLNL has begun integrating the new AI hardware,…
With funding from the Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security (CARES) Act, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), chipmaker AMD and information technology company Supermicro have upgraded the supercomputing cluster Corona, providing additional resources to scientists for COVID-19 drug discovery and vaccine research. The recent addition of nearly 1,000 AMD…
Construction crews recently wrapped up a long-anticipated electrical system upgrade that will supply Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and neighboring Sandia/California with reliable, redundant underground power, completing it months ahead of schedule and well under budget. The first line-item project for LLNL in more than a decade, the Expand Electrical…
In recognition of Manufacturing Day 2020 (MFG DAY) on Oct. 2, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) will host a special online webinar to discuss the impact of the High Performance Computing for Energy Innovation (HPC4EI) initiative on American industrial competitiveness and energy savings. The virtual event begins at 8 a.m. PDT/11 a.m. EDT and is highlighted by a…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and artificial intelligence (AI) computer company Cerebras Systems have integrated the world’s largest computer chip into the National Nuclear Security Administration’s (NNSA’s) Lassen system, upgrading the top-tier supercomputer with cutting-edge AI technology. Technicians recently completed connecting the Silicon Valley-based…
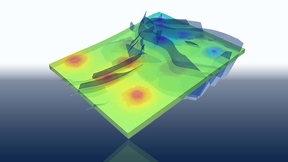
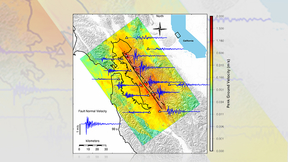
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team has published new supercomputer simulations of a magnitude 7.0 earthquake on the Hayward Fault. This work represents the highest-ever resolution ground motion simulations from such an event on this scale. The study used the SW4 code developed at LLNL. Simulations resolved rapidly varying shaking with broader band…
One of the most common congenital heart defects, coarctation of the aorta (CoA) is a narrowing of the main artery transporting blood from the heart to the rest of the body. It affects more than 1,600 newborns each year in the United States, and can lead to health issues such as hypertension, premature coronary artery disease, aneurysms, stroke and cardiac failure. To…