Back
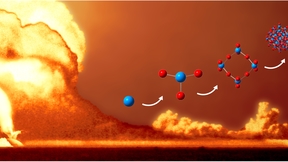
TATB (1,3,5-triamino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene) is an important explosive compound because of its extensive use in munitions and world-wide weapons systems. Despite its importance, researchers have been trying to understand its response to temperature extremes for the past 50 years. A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team has uncovered a new thermal decomposition…
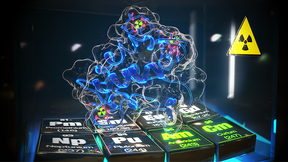
Past and present nuclear activities (energy, research and weapon tests) have increased the need to understand the behavior of radioactive materials in the environment. Nuclear wastes containing actinides (such as plutonium, americium, curium and neptunium) are particularly problematic as they remain radioactive and toxic for thousands of years. However, when compared to…
While neutrinos are one of the most common particles in the universe, their elusive nature makes it challenging to understand their behavior. In new research from the Precision Reactor Oscillation and Spectrum (PROSPECT) Experiment, scientists have produced final results from measurements of neutrinos emitted by a nuclear reactor at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Their…
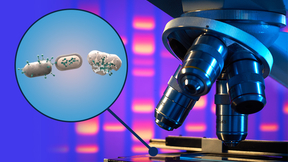
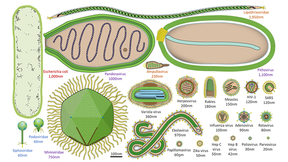
Beneath the Earth's surface, a relentless conflict unfolds as soil viruses prey on their tiny microbial hosts, fundamentally shaping our planet's ecosystems. New research from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and their collaborators at the University of California, Berkeley illuminates a fascinating phenomenon: the demise of soil bacteria and other…
The groundbreaking discoveries and scientific advancements that take place at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and across the broader national laboratory system rely on the passage of information from tenured staff scientists to new interns and early career scientists. This past summer, Zachary (Zach) Murphy, a Ph.D. student studying chemistry at the…
An instrument designed and built by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers departed Earth last week on a two-billion-mile, nearly six-year journey through space to explore a rare, largely metal asteroid. The Livermore high-purity germanium (HPGe) gamma-ray sensor is an essential part of a larger gamma-ray spectrometer (GRS) built in collaboration with…
Miguel Cisneros is a first-generation Mexican American whose journey in life has taken him to explore and navigate the unknown fearlessly. Growing up, Cisneros was an only child who welcomed new adventures. His interest in exploring new experiences and places is something he continues to do to this day. Cisneros’ parents migrated from Mexico to the United States for a…
Two graduate students have earned Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science Graduate Student Research (SCGSR) Program awards to perform their doctoral dissertation research at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). The prestigious award helps cover living expenses and travel for 60 students from universities across the nation. Their proposed research projects…
Neutron-capture reactions on unstable nuclei play a key role in the production of heavy elements in the universe and provide vital diagnostics for reaction networks related to stockpile stewardship. However, these reactions cannot be measured directly because they involve radioactive nuclei. Lawrence Livermore researchers have performed indirect measurements to constrain…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists will lead and co-lead projects in support of the Department of Energy’s (DOE) new Energy Earthshot program. The Energy Earthshots Initiative calls for innovation and collaboration to tackle the toughest topics in energy-related research. In January, DOE announced Office of Science funding for the Energy Earthshot…
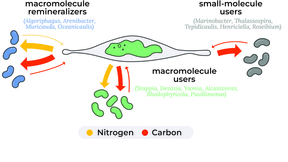
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists have found that bacteria can help algae make carbon-neutral biofuels or draw down additional carbon from the atmosphere if the conditions are just right. The team used LLNL’s nanoSIMS to understand and quantify the role of the algal microbiome in processing algal carbon (C) and nitrogen (N). The research appears in…
In the quest to understand how nuclear debris forms, a team of scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) has developed an approach to studying the oxidation mechanism of gas phase uranium in extreme environments. In research recently published in Scientific Reports, the team outlined their work, which combined experimental data from a plasma flow reactor …
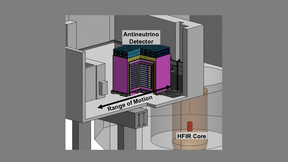
Nuclear reactors, among the brightest terrestrial emitters of antineutrinos, have been central to neutrino physics. For more than a decade, physicists have puzzled over anomalous differences between measurements and predictions of the antineutrino emissions from nuclear reactors. These differences could reveal deficiencies in prediction methods and their underlying nuclear…
Two scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) are recipients of the Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Science Early Career Research Program award. Daniel Casey and Gauthier Deblonde are among 93 awardees receiving the recognition. Under the program, typical awards for DOE national laboratory staff are $500,000 per year for five years. “Supporting…
An international collaboration of researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and other scientific institutions is ramping up its studies into “sterile neutrinos” to discover and better understand dark matter. Sterile neutrinos are theoretically predicted new particles that offer an intriguing possibility in the quest for understanding the dark matter in…
Cropland management practices that restore soil organic carbon (SOC) are often looked at as climate solutions that also enhance yields. But how often these benefits align at the farm level — the scale of farmers’ decision-making — remains unclear. In a new study in Nature Sustainability, a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientist and collaborators examined…
Three graduate students have earned Department of Energy Office of Science Graduate Student Research (SCGSR) Program awards to perform their doctoral dissertation research at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). They are three among the 87 graduate students representing 33 states for the SCGSR program’s 2022 Solicitation 2 cycle. Through world-class training and…
On Earth, viruses are abundant and an integral part of life. However, very little is known about them outside human health contexts, especially in areas related to space. Understanding the role viruses play on Earth and how they interact with their hosts in extreme environments can better inform human spaceflight missions (environmental control, life support systems, and…
Studying radioactive materials is notoriously difficult due to their radiation-induced toxicity and risk of contamination when handling. The cost of the radioactive isotopes used in research also is a major barrier, with some costing more than $10,000 per microgram. Certain radioisotopes also cannot be produced in sufficient quantity so it is simply impossible for…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) employees, participating in five project teams, recently earned Department of Energy (DOE) Secretary’s Honor Achievement Awards. Representing some of the highest internal, non-monetary recognition that DOE employees and contractors can receive, the Secretary’s Honor Awards recognize DOE employees and contractors for their…