Back
The earliest solids formed in the solar system give clues to what radioactive species were made by the young sun, and which ones were inherited. By studying isotopic variations of the elements vanadium (V) and strontium (Sr), an international team of researchers including scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) found that those variations are not…
The Post-Detonation Rapid Response Research Venture — also known as R-cubed or R3 — is combining basic research and development of emergent technologies, predictive capabilities and systems assessment to revolutionize the speed and flexibility of technical nuclear forensic (TNF) response to nuclear events. The venture is a multi-laboratory collaboration led by Lawrence…
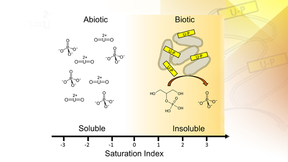
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and collaborators have proposed a new mechanism by which nuclear waste could spread in the environment. The new findings, which involve researchers at Penn State and Harvard Medical School, have implications for nuclear waste management and environmental chemistry. The research is published in the Journal of the…
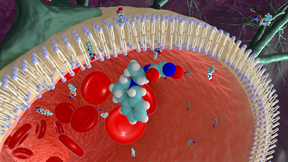
Scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have developed a new, versatile antidote to counteract exposure to nerve agent poisoning. The work, appearing in the journal Scientific Reports, was the result of a highly iterative process built in collaboration between LLNL’s Global Security Directorate, its Forensic Science Center and the U.S. Army Medical…
Editor’s note: The following is part of a series of articles looking back at the Lab's response immediately following the Sept. 11 attacks and our contributions since that day 20 years ago. From keeping Americans safe at national events to assisting with international disasters, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL) National Atmospheric Release Advisory Center …
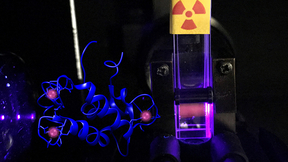
It wasn’t an easy road, but Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) Forensic Science Center scientists earned an “A” grade in the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons’ (OPCW) recent biomedical proficiency test. In addition to the usual complexity of the sample preparations and analysis, the Livermore scientists received their proficiency test samples…
This fall, a score of scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's (LLNL) Forensic Science Center (FSC) will start two weeks of long days to undertake the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) environmental proficiency test. Livermore scientists have been taking the proficiency tests each October since 2001, with LLNL serving as one of two…
How could life begin from a swirling chaos? How did Earth and its moon form? What can lunar rocks from the Apollo missions reveal? And what will scientists learn from exploration on distant moons? These questions are addressed in this four-part feature article on Lawrence Livermore’s space science research.
Just a few bacterial groups found in ecosystems across the planet are responsible for more than half of carbon cycling in soils, according to new findings from researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Northern Arizona University, published in Nature Communications. The new research suggests that despite the diversity of microbial taxa found in wild…
Two scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) are recipients of the 2021 Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Science Early Career Research Program award. Andrea Schmidt and Xue Zheng are among 83 scientists nationwide selected for the recognition. Under the program, typical awards for DOE national laboratory staff are $500,000 per year for five years…
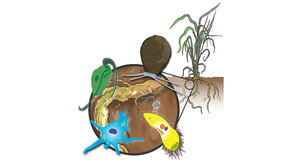
Plants evolved in a world dominated by prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbes. Underneath the surface, plant roots interact with microbes in the soil, also called the rhizosphere microbiome. Although bacteria and fungi are well-studied in the rhizosphere (the layer closest to the roots), other components, including viruses and protists, are less well known. A protist is any…
Uranium contamination of soils and groundwater in the United States represents a significant health risk and will require multiple remediation approaches. Remediation strategies for uranium-contaminated sites have been the focus of research for decades due to the former production of nuclear materials across the United States. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)…
Penn State graduate student Joseph Mattocks has been selected to serve at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory as part of the Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Science Graduate Student Research (SCGSR) Program. Mattocks will serve in LLNL's Nuclear and Chemical Sciences Division. “I feel both honored and grateful to have been given this opportunity to pursue a…
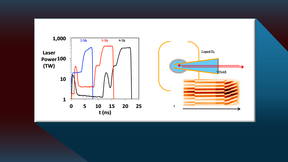
In inertial confinement fusion (ICF) experiments at the National Ignition Facility (NIF), a spherical shell of deuterium-tritium fuel is imploded in an attempt to reach the conditions needed for fusion, self-heating and eventual ignition. Since theory and simulations indicate that ignition efficacy in one-dimension (1D) improves with increasing imploded fuel convergence…
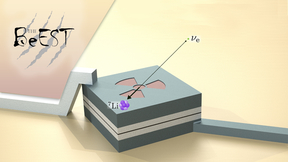
“Sterile neutrinos” are theoretically predicted new particles that offer an intriguing possibility in the quest for understanding the dark matter in our universe. Unlike the known “active” neutrinos in the Standard Model (SM) of particle physics, these sterile neutrinos do not interact with normal matter as they move through space, making them very difficult to detect. A…
Three Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) postdoctoral appointees have been selected to attend the 70th annual Lindau Nobel Laureate meeting in Germany this June thanks to the University of California President’s 2021 Lindau Nobel Laureate Meetings Fellows Program. The three selected to attend the meeting are Oluwatomi (Tomi) Akindele, Matthew Edwards and Wei Jia…
Researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and their colleagues who help them commercialize technologies have won three national technology transfer awards this year. The trio of awards, from the Federal Laboratory Consortium (FLC), represent the most national awards that LLNL has ever won in one year’s competition over the past 36 years. Two of the…
Elevated carbon dioxide emissions from human activities increase the uptake of carbon by plants but may decrease storage in soil. An international team led by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists synthesized 108 elevated carbon dioxide (CO2) experiments in various ecosystems to find out how much carbon is absorbed by plants and soil. The research…
What are the next world-class, game-changing concepts and technologies that will address the most important questions in astrophysics or planetary science? Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers will soon be better equipped to answer this question with the launch this month of a new Space Science Institute (SSI), intended to boost cross-discipline…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) employees, participating in 10 project teams, recently earned Department of Energy (DOE) Secretary Achievement Awards. Representing some of the highest internal, non-monetary recognition that DOE employees and contractors can receive, these awards recognize DOE employees and contractors for their service and contributions to…