Back
LLNL’s Materials Science Division (MSD) recently hosted an open house showcasing its lab facilities and redesigned workspaces that support the division’s expanding research scope. The event, led by Division Leader Manyalibo (Ibo) Matthews, featured tours of updated laboratory spaces. At each tour stop, MSD scientists provided a brief overview of the research that takes…
A new study provides surprising behavior of hydrogen bonding of water confined in carbon nanotubes. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists combined large-scale molecular dynamics simulations with machine learning interatomic potentials derived from first-principles calculations to examine the hydrogen bonding of water confined in carbon nanotubes (CNTs)…
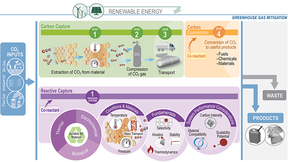
To date, most CO2 capture and conversion processes have been developed in isolation, where the output of the capture process is purified, compressed CO2, which can be used as the feedstock for the CO2 conversion process. This is an energy intensive process and purified CO2 stream still needs to be delivered to the location where it will be converted to the desired product,…
The need for efficient and sustainable energy storage systems is becoming increasingly crucial as the world transitions toward renewable energy sources. However, traditional energy storage systems have limitations, such as high costs, limited durability, and low efficiency. Therefore, new and innovative materials and technologies, such as aerogels (highly porous networks…
In virtual ceremonies held May 4 and June 26, Marvin Adams, deputy administrator for Defense Programs at the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), honored individuals and teams at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and partner sites for their outstanding contributions to nuclear security. The Defense Programs Awards of Excellence recognition events…
Optics researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have refined their novel metasurface process to create taller features without increasing feature-to-feature spacing, an advance that unlocks exciting new design possibilities. “We have refined our process to create metasurfaces that allow for a wide optical bandwidth and a large span of incidence angles…
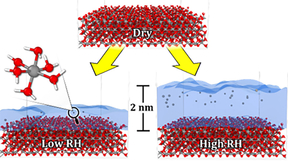
Scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) performed simulations using the Lab's supercomputer Ruby to uncover physical mechanisms that explain why humidity controls the rate of atmospheric corrosion of aluminum metal. Their research is featured in the ACS Journal of Applied Materials and Interfaces. Accurate predictions of aluminum component lifetimes…
Six scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory were recently granted awards through the Lab's 2022 Academic Collaboration Team (ACT) annual call for proposals. Now in their fourth year, ACT university collaboration awards were created to encourage and advance strategic partnerships among universities with a focus on the Lab’s and Weapons and Complex Integration’s…
Lizz Lantz has always been driven by curiosity about how the world works. “I’m really interested in the materials that make up the world around us, which we often take for granted,” Lizz Lantz said. “And, what better way to explore the world’s fabric than to inspect it under the microscope?” Lizz Lantz exercises this interest in her position as a metallography technician…
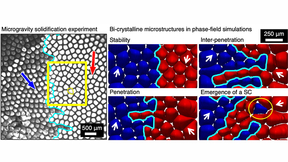
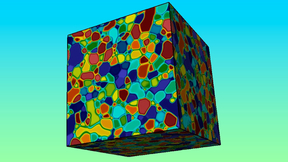
In solidification processing, such as casting, welding, or additive manufacturing, cellular or dendritic patterns develop during the growth of a solid crystal from the liquid phase. In metallurgy, each similarly patterned region is referred to as a grain—which must be controlled during processing as grains affect structural performance. Additionally, the grain texture—the…
Copper-based catalysts are highly active for electrochemical reduction of CO2 (CO2R) to several desirable hydrocarbon products, such as methane (CH4), formic acid (HCOOH), ethylene (C2H4), and ethanol (C2H5OH). CO2R is dually beneficial, as it allows for the conversion of excess atmospheric CO2 into useful chemicals. However, using copper-based catalysts for CO2R depends…
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL)-developed technology known as Energy Inks has won a best in region award for the Far West region from the Federal Laboratory Consortium for Technology Transfer (FLC). This is the technology’s second award in the past nine months, as it received an R&D 100 award last September as one of the top 100 industrial inventions in…
Titanium (Ti) and its alloys are attractive for a wide variety of structural and functional applications due to the metal’s excellent strength, toughness and stiffness, and corrosion resistance. Specific applications include lightweight structural materials, bioimplants, and energy storage materials. However, if exposed to hydrogen sources, these alloys are susceptible to…
Part 8 in a series of articles describing the elements of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's fusion breakthrough. The intricate, delicate targets used in Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL)’s National Ignition Facility (NIF) experiments are marvels of design, engineering and precise manufacturing. “We’ve been working over the last 16 years on continuously…
In 1888, Walther Nernst proposed a universal relation between a charged particle’s electrophoretic mobility (a solute’s velocity in response to an applied electric field) and its diffusion coefficient (the rate at which a particle free-diffuses through medium). The microscopic origins of this relation were revealed in 1905 by Albert Einstein. These works cemented the…
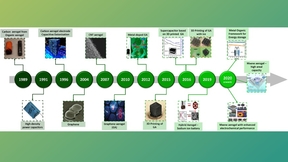
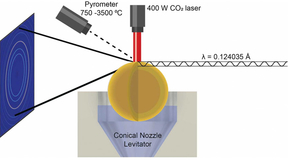
There is a growing interest in understanding the performance and properties that make ultra-high temperature ceramics (UHTCs) promising for extreme environment applications, such as hypersonic platforms, nuclear reactors, and atmospheric re-entry. UHTCs are inorganic materials that exhibit metallic conductivity with melting temperatures above 3000 °C. One such material,…
Four Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) postdoctoral appointees have been selected to attend the 72nd annual Lindau Nobel Laureate meeting in Germany this summer thanks to the University of California President’s 2023 Lindau Nobel Laureate Meetings Fellows Program. The four selected to attend are Wonjin Choi, Sean Leonard, Sijia Huang and Sarah Sandholtz. The…
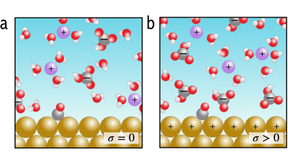
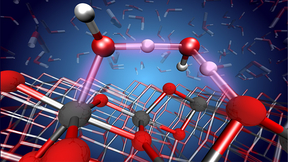
Through machine learning, a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientist has a better grasp of understanding materials used to produce hydrogen fuel. Water is everywhere in the environment and its interaction with metal oxide surfaces has a key role in processes that range from wetting, dissolution and corrosion to photocatalytic reactions. The relative…
Part 5 in a series of articles describing the elements of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's fusion breakthrough. If Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL)’s National Ignition Facility (NIF) were a race car, it would run at the redline most of the time. “NIF is the only laser system that intentionally operates above the laser damage growth threshold,” said…
When it comes to studying particles in motion, experimentalists have followed a 100-year-old theory that claims the microscopic motion of a particle is determined by random collisions with molecules of the surrounding medium, regardless of the macroscopic forces that drive that motion. Scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and the Massachusetts…