Back
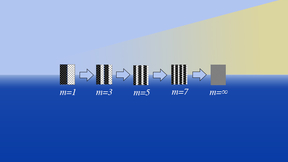
Research conducted at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is taking a closer look at entropy — the measure of internal energy per unit temperature that is unavailable for doing useful work — in experiments at the National Ignition Facility (NIF). Work by LLNL physicist Peter Amendt is highlighted as an Editor’s Pick in Physics of Plasma, showing that an added…
The announcement that the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO) had detected gravitational waves during the merger of two black holes sent ripples throughout the scientific community in 2016. The earthshaking news not only confirmed one of Albert Einstein’s key predictions in his general theory of relativity, but also opened a door to a better…
For much of the past decade, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have been designing major optical components for the world’s newest telescope, while their industrial partners have fabricated the components. Now, with the September shipment of the last of six optical filters for the telescope’s camera to the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory in…
Three Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) physicists have been selected as 2021 fellows of the American Physical Society (APS). The new fellows represent a selection of physics expertise, ranging from intense laser-matter interactions and inertial fusion energy science to leading the development of edge simulation models and codes to pioneering new regimes of…
New research involving Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists shows that water can remain liquid in a metastable state when transitioning from liquid to a dense form of ice at higher pressures than previously measured. Water at extreme conditions has attracted recent attention because of its complex phase diagram, including superionic ice phases having…
Volcanic eruptions spew lava, rock and ash into the air. When fragments of these materials mix and collide in the outflow, they can create an electric potential large enough to generate lightning. New research by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and collaborators discovered that standing shock waves in the supersonic outflow of gases prevent…
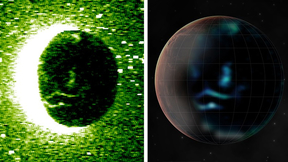
The interiors of Uranus and Neptune each contain about 50,000 times the amount of water in Earth’s oceans, and a form of water known as superionic water is believed to be stable at depths greater than approximately one-third of the radius of these ice giants. Superionic water is a phase of H2O where hydrogen atoms become liquid-like while oxygen atoms remain solid-like on…
The United Arab Emirates' (UAE) Mars mission that launched about a year ago has recently captured the most detailed images of auroras in the Martian sky. The optics used to capture these images include a silicon carbide-coated mirror and diffraction grating for the Emirates Mars Ultraviolet Spectrometer (EMUS) that were developed by researchers at Lawrence Livermore…
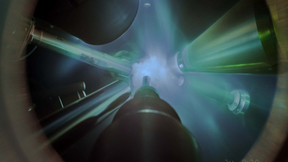
On Aug. 8, 2021, an experiment at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL’s) National Ignition Facility (NIF) made a significant step toward ignition, achieving a yield of more than 1.3 megajoules (MJ). This advancement puts researchers at the threshold of fusion ignition, an important goal of the NIF, and opens access to a new experimental regime. The experiment…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have explored high-pressure behavior of shock-compressed tantalum at the Omega Laser Facility at the University of Rochester’s Laboratory for Laser Energetics (LLE). The work showed tantalum did not follow the predicted phase changes at high pressure and instead maintained the body-centered cubic (BCC) phase until…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists have experimentally tested the predictions of a 2020 study that computationally investigated the effect of melting on shock driven metal microjets. That earlier work predicted that melting the base material does not necessarily lead to a substantial increase in jet mass. The LLNL team confirmed the predictions of…
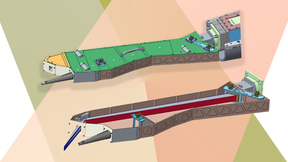
Scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have collaborated with Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) to design a novel X-ray crystal spectrometer to provide high-resolution measurements of a challenging feature of high energy density (HED) matter produced by National Ignition Facility (NIF) experiments. The work is featured in a paper in the Review…
Thousands of images of Earth and space have been taken by a compact space imaging payload developed by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers and its collaborator Tyvak Nano-Satellite Systems. Known as GEOStare2, the payload has two space telescopes that together have taken more than 4,500 pictures for space domain awareness, astronomy and Earth…
The properties of materials under extreme conditions are of key interest to a number of fields, including planetary geophysics, materials science and inertial confinement fusion (ICF). In geophysics, the equation of state of planetary materials such as hydrogen and iron under ultrahigh pressure and density will provide a better understanding of their formation and interior…
Federica Coppari uses the world’s most powerful laser to recreate the cores of distant worlds.
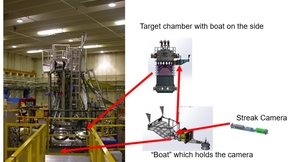
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Sandia National Laboratories continue to collaborate on diagnostic advancements on the nation’s premier high-energy density (HED) facilities. Mark Bowers, magnetic direct drive diagnostics manager at the National Ignition Facility (NIF), said current projects include providing NIF’s X-ray streak camera, neutron Time-of…
To test the Standard Model of particle physics, scientists often collide particles using gigantic underground rings. In a similar fashion, high-pressure physicists compress materials to ever greater pressures to further test the quantum theory of condensed matter and challenge predictions made using the most powerful computers. Pressures exceeding 1 million atmospheres are…
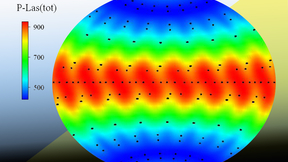
Scientists have examined the performance of pure boron, boron carbide, high-density carbon and boron nitride ablators — the material that surrounds a fusion fuel and couples with the laser or hohlraum radiation in an experiment — in the polar direct drive exploding pusher (PDXP) platform, which is used at the National Ignition Facility (NIF). The platform uses the polar…
Nearly 40 years ago, scientists first predicted the existence of helium rain inside planets composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, such as Jupiter and Saturn. However, achieving the experimental conditions necessary to validate this hypothesis hasn’t been possible — until now. In a paper published today by Nature, scientists reveal experimental evidence to support this…
While advances in machine learning over the past decade have made significant impacts in applications such as image classification, natural language processing and pattern recognition, scientific endeavors have only just begun to leverage this technology. This is most notable in processing large quantities of data from experiments. Research conducted at Lawrence Livermore…