Back
Like a game of "hide and seek," Lawrence Livermore astrophysicists know that there are black holes hiding in the Milky Way, just not where. If they find them toward the galactic bulge (a tightly packed group of stars) and the Magellanic Clouds, then black holes as massive as 10,000 times the mass of the sun might make up dark matter. If they are only toward the galactic…
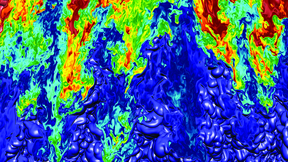
In a Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) "Special Feature" paper published online June 26, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and University of Michigan researchers reported on recent experiments and techniques designed to improve understanding and control of hydrodynamic (fluid) instabilities in high energy density (HED) settings such as…
The program to extend the life of the W80 nuclear warhead recently achieved a significant milestone when the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) gave passing grades to the plans to refurbish certain components and the proposed approach to developing component cost estimates. Passing the milestone confirms that the life extension program (LEP), dubbed the W80-4…
Retiree Bruce Cohen (PHYS) has been selected as the recipient of the 2018 IEEE Nuclear and Plasma Sciences Society’s Charles K. Birdsall Award for “contributions to the numerical simulation of plasmas, particularly multiple time-scale methods, and to their application to diverse plasma physics problems, from laser–plasma interactions to tokamaks.” The Birdsall Award…
When Michael Campanell was a graduate student at the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory, he noticed something unusual: the boundary physics simulation he was running wasn’t behaving the way it was supposed to. A century of plasma theory predicted one thing, but Campanell’s simulation was doing another. This was the impetus for his thesis, and a big challenge to the status…
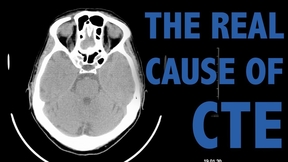
Researchers have identified evidence of early chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) brain pathology after head impact -- even in the absence of signs of concussion. Early indicators of CTE pathology not only persisted long after injury but also spread through the brain, providing the best evidence to date that head impact, not concussion, causes CTE. The findings,…
Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) released 62 newly declassified videos today of atmospheric nuclear tests films that have never before been seen by the public. The videos are the second batch of scientific test films to be published on the LLNL YouTube channel this year, and the team plans to publish the remaining videos of tests conducted by…
Unaided and under the darkest conditions, the human eye can see only about 9,000 stars around Earth. The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST)—looking at only half of the night sky—is expected to detect an estimated 17 billion stars and discover so much more over the course of a 10-year mission.
Mars’ largest moon, Phobos, has captured public imagination and been shrouded in mystery for decades. But numerical simulations recently conducted at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have shed some light on the enigmatic satellite. The dominant feature on the surface of Phobos (22-kilomters across) is Stickney crater (9-km across), a mega crater that spans…
When Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory physicist Maxim Umansky flipped through the news, a startling underwater survival story caught his attention. In May, a boat cook survived a 60-hour underwater ordeal 100 feet below the surface after his tugboat sank near the Nigerian coast.Harrison Okene's survival underwater while the rest of the crew perished was astounding…