Back
An international team of scientists has found new biomarkers that can be used for diagnostic purposes and potentially as predictive tools of the risks associated with deep-space flight. In their study, the team, including three researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), examined approximately two-decade-old blood samples from space shuttle astronauts…
The Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) Early Career Research Program (ECRP) aims to bolster the nation’s scientific workforce by providing support to exceptional researchers at U.S. academic institutions and DOE’s national laboratories during their early career years. Annually, ECRP provides research funding to full-time staff in their first 10 years post-doctorate.
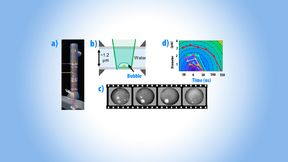
The formation and collapse of microscopic bubbles is important in a wide range of fields as both a potential mechanism behind tissue damage, such as in cases of blast-wave-induced traumatic brain injury, and as a useful tool for technology applications, such as mechanical properties evaluation, nanomaterials manipulation and surface cleaning. Nanobubbles have been of…
Antibiotics have allowed for the widespread control of bacterial infections, which had been the leading cause of death historically. However, the overuse of traditional antibiotics in humans and animals resulted in the emergence of stronger, more potent bacterial strains that are no longer treatable with conventional antibiotics. Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National…
Scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and three other institutions are seeking to develop a multi-pathogen vaccine that will protect against three bacterial biothreat pathogens. Led by LLNL, the team includes disease experts from the University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center (UNMHSC), the University of Nevada, Reno School of Medicine (UNR Med)…
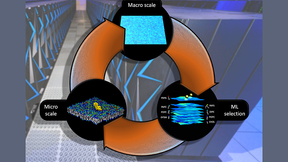
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers and a multi-institutional team of scientists have developed a highly detailed, machine learning-backed multiscale model revealing the importance of lipids to the signaling dynamics of RAS, a family of proteins whose mutations are linked to numerous cancers. Published by the Proceedings of the National Academy of…
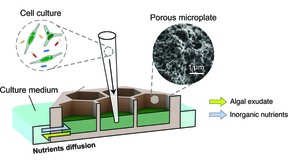
Microscopic algae are responsible for half of the global atmospheric carbon fixed from the atmosphere through photosynthesis, and may be used as a sustainable bioenergy source. The water immediately outside their cells, called the “phycosphere,” is rich with algal-excreted organic carbon, and is an ideal ecosystem for bacterial growth. However, detecting and measuring…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL’s) fifth annual Research Slam! took place virtually on October 6th and featured 14 LLNL postdocs, 9 of which represented the Physical and Life Sciences Directorate (PLS). Over 300 people logged on to attend the live two-hour event, enthusiastically cheering for their favorite postdocs in the comment section. Each finalist was…
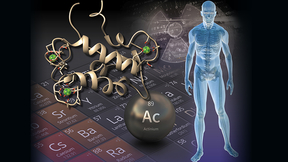
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Penn State scientists have demonstrated how a protein can be recovered and purified for radioactive metals like actinium that could be beneficial for both next-generation drugs used in cancer therapies and the detection of nuclear activities. Radioactive metals hold unique and essential places in a variety of medical…
The top winners of the recent Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) Research Slam!, a speaking competition for postdocs, will advance to the Bay Area Research SLAM set for Thursday, Oct. 28. The Bay Area Research SLAM! is a collaboration between the Bay Area’s national labs (Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, LLNL, Sandia National Laboratories and SLAC National…
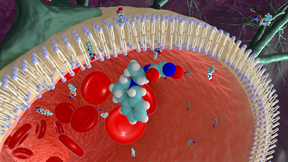
Scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have developed a new, versatile antidote to counteract exposure to nerve agent poisoning. The work, appearing in the journal Scientific Reports, was the result of a highly iterative process built in collaboration between LLNL’s Global Security Directorate, its Forensic Science Center and the U.S. Army Medical…
A team led by LLNL scientists has discovered the first antidote against nerve-agent poisoning that crosses the blood–brain barrier (BBB). Their research, published in Scientific Reports, comes on the heels of a recent resurgence of nerve agents in transnational conflicts. Organophosphorus-based nerve agents (OPNAs)—including sarin, soman, and VX—cross the BBB and are…
Recent advances in body armor and other battlefield damage control strategies have increased the proportion of survivable blast-related combat injuries. Over the last few decades, treatment of warfighters surviving increasingly severe injuries has created new challenges across the Department of Defense’s Military Health System.
Long before the COVID-19 pandemic gripped the globe, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory had been preparing to help the nation contend with biological threats. From its inception, Livermore has focused its scientific and technological expertise on strengthening the security of the United States.
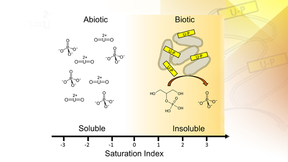
Uranium contamination of soils and groundwater in the United States represents a significant health risk and will require multiple remediation approaches. Remediation strategies for uranium-contaminated sites have been the focus of research for decades due to the former production of nuclear materials across the United States. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is looking for participants and attendees from industry, research institutions and academia for the first-ever Machine Learning for Industry Forum (ML4I), a three-day virtual event starting Aug. 10. Pre-registrations are open for the forum, which aims to foster and illustrate the adoption of machine learning methods for…
COVID-19 HPC Consortium scientists and stakeholders met virtually on March 23 to mark the consortium’s one-year anniversary, discussing the progress of research projects and the need to pursue a broader organization to mobilize supercomputing access for future crises. The White House announced the launch of the public-private consortium, which provides COVID-19 researchers…
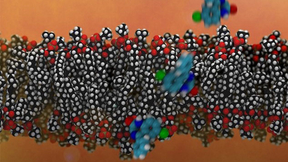
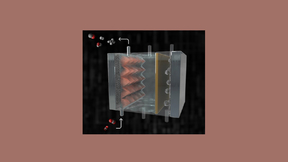
Using carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions to create value-added products is an attractive approach to reduce net greenhouse gas emissions. Processes such as the electrochemical reduction of CO2 to ethylene and ethanol offer a pathway to producing commodity chemicals without fossil fuels when they are powered using low-carbon electricity. Gas diffusion electrode (GDE) assemblies…
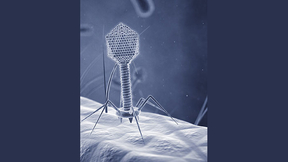
Scientists in the Forensic Science Center at Lawrence Livermore have partnered with San Diego State University and UCSD to advance bacteriophage therapy.
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists are leveraging their extensive experience studying the movement of airborne hazards to better understand the movement of virus-like particles through the air and to identify effective countermeasures. DNATrax released in a conference room.While the burden of airborne diseases is known to be large, its true scope is…