Back
Philip Adams, chief technical officer for Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL) National Ignition Facility (NIF), has been recognized with a 2018 Oracle Excellence Award. The annual program recognizes customers and partners for exceptional use of Oracle solutions to accelerate innovation and drive business transformation and value by increasing agility, lowering…
The Nobel Prize-winning research by Donna Strickland, a former staff scientist in Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's (LLNL’s) Laser Programs Directorate, was instrumental in the Laboratory’s development of a series of groundbreaking short-pulse, high-energy laser systems over the past two decades. Self-described "laser jock" Strickland, who worked at LLNL in 1992, is…
The moment Louisa Pickworth saw the rings of Saturn through her father’s backyard telescope, she knew she wanted to become a scientist to learn "more and more and more." Today, Pickworth, 32, is one of LLNL’s heralded young physicists for her work developing cutting-edge X-ray diagnostics to help scientists learn more about ultrahigh energy physics and inertial confinement…
Four Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have been named Distinguished Members of Technical Staff (DMTS) for their extraordinary scientific and technical contributions to the Laboratory and its missions, as acknowledged by their professional peers and the larger community. Peter Beiersdorfer and Paul Springer of the Physical and Life Sciences…
A group of NIF & Photon Science summer scholars and visiting graduate students are experiencing the value of teamwork as they conduct experiments at LLNL’s Jupiter Laser Facility (JLF). Jesus Hinojosa, 26, a University of Michigan graduate student, and Matthew Thibodeau, 21, a Rice University undergraduate, joined a team of veteran scientists and researchers to explore…
Swirling dense metallic hydrogen dominates the interiors of Jupiter, Saturn and many extra-solar planets. Building precise models of these giant planets requires an accurate description of the transition of pressurized hydrogen into this metallic substance — a long-standing scientific challenge. In a paper published today by Science, a research team led by scientists at…
In a Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) "Special Feature" paper published online June 26, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and University of Michigan researchers reported on recent experiments and techniques designed to improve understanding and control of hydrodynamic (fluid) instabilities in high energy density (HED) settings such as…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL) National Ignition Facility (NIF) laser system has set a new record, firing 2.15 megajoules (MJ) of energy to its target chamber -- a 15 percent improvement over NIF’s design specification of 1.8 MJ, and more than 10 percent higher than the previous 1.9 MJ energy record set in March 2012. This demonstration shot successfully…
After evaluation by an international peer review group, the L3-HAPLS advanced petawatt laser system has been declared fully integrated and operational at the ELI Beamlines Research Center in Dolní Břežany, Czech Republic. The group assessed the laser performance, determined that all performance parameters have been successfully met -- capable of reaching the 1 petawatt, 10…
Tammy Ma, a plasma physicist at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), has been named a recipient of the prestigious Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science Early Career Research Program (ECRP). The program, now in its ninth year, is designed to bolster the nation’s scientific workforce by providing support to exceptional researchers during the crucial early…
Marius Millot was just a child when scientists at the University of Pennsylvania and Los Alamos National Laboratory predicted the existence of superionic water ice using molecular dynamics simulations. This new phase of water is characterized by the liquid-like diffusion of hydrogen ions within the solid lattice formed by the oxygens. For three decades, superionic ice…
An experimental campaign conducted at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL) National Ignition Facility (NIF) has achieved a total fusion neutron yield of 1.9e16 (1.9x1016) and 54 KJ of fusion energy output -- double the previous record. Researchers in LLNL’s Inertial Confinement Fusion Program (ICF) detail the results in a paper that will be published this week…
Boiling water traditionally involves adding energy to molecules by conduction, convection or thermal radiation. But Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and collaborators have figured out a way using an X-ray Free Electron Laser (XFEL) to heat water to temperatures above 100,000 K (179,540 degrees Fahrenheit) and pressures above 1Mbar (1 million times…
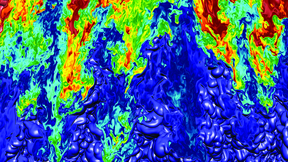
Experiments on Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's National Ignition Facility (NIF) are providing scientists with new insights into the turbulent after-effects of a supernova explosion. The studies also could inform efforts to achieve self-sustaining nuclear fusion on NIF and other high-energy laser systems. When stars of a certain mass collapse and then violently…
Using high-powered laser beams, iron-silicon alloys have been compressed to unprecedented pressures corresponding to the center of a three-Earth-mass extrasolar planet. The resulting measurements of crystal structure and density provide new insights into the nature of the deep interiors of the large, Earth-like planets that have been discovered throughout our galaxy. The…
In a paper published today by Nature Astronomy, a team of researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), Princeton University, Johns Hopkins University and the University of Rochester have provided the first experimentally based mass-radius relationship for a hypothetical pure iron planet at super-Earth core conditions. This discovery can be used to…
Nearly 20 years ago, researchers conducting experiments on Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's (LLNL) Nova Petawatt laser system -- the world’s first quadrillion-watt laser -- discovered that when the system’s intense short-pulse laser beams struck a thin foil target, an unexpected torrent of high-energy electrons and protons streamed off the back of the target…
In 2017, after more than eight years of operation, the National Ignition Facility (NIF) at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) reached its epic 2,000th shot. Over that time, as the shot rate steadily climbed, other important numbers also have risen dramatically. By the end of 2017, the total number of people exposed first-hand to NIF’s world-class technology and…
Among the many discoveries on matter at high pressure that garnered him the Nobel Prize in 1946, scientist Percy Bridgman discovered five different crystalline forms of water ice, ushering in more than 100 years of research into how ice behaves under extreme conditions. One of the most intriguing properties of water is that it may become superionic when heated to several…
Henry Chapman, who worked at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) from 1996 to 2007, will be presented on Jan. 26 with an honorary doctorate by Sweden's Uppsala University for his work on developing techniques for imaging and crystallography with intense X-ray pulses. In addition to lecturing as a professor of physics at Hamburg University, Chapman is the division…