Back
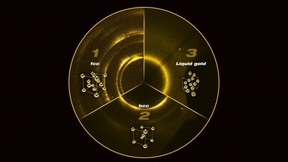
Gold is an extremely important material for high-pressure experiments and is considered the "gold standard" for calculating pressure in static diamond anvil cell experiments. When compressed slowly at room temperature (on the order of seconds to minutes), gold prefers to be the face-centered cubic (fcc) structure at pressures up to three times the center of the Earth…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists Félicie Albert, Eyal Feigenbaum and Bruce Warner have been named senior members of the Optical Society (OSA), an international organization for optics and photonics scientists, engineers, educators and business leaders. Senior membership status recognizes members with more than 10 years of professional experience in…
Research authored by physicists in Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's National Ignition Facility & Photon Science Directorate (NIF&PS) represented four of the prestigious Physics of Plasmas' top 10 list of "most cited papers" of 2018. The papers on the list have accumulated five or more citations, according to AIP (American Institute of Physics) Publishing…
Crystal growth is a crucial issue for fundamental science and wide applications. The growth morphology and speed are generally determined by an interplay between macroscopic thermodynamic driving forces and the microscopic kinetic process at crystal-liquid interface. While crystal growth is well understood at near-equilibrium growth conditions, the growth transition with…
Gold, silver and copper are heavy metals, but LLNL scientists can now make them nearly as light as air — in a form so tiny it can ride on a mosquito’s back. The groundbreaking science, part of a joint NIF/Physical and Life Sciences (PLS) project supported by the Laboratory Directed Research and Development (LDRD) Program, created these ultra-low density metal foams to give…
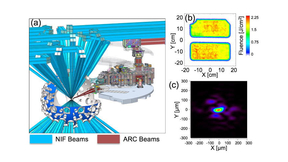
The first proton-acceleration experiments using the National Ignition Facility’s (NIF) Advanced Radiographic Capability (ARC) short-pulse laser have produced protons with energies about 10 times higher than previous experience would have predicted (see "A Powerful New Source of High-Energy Protons"). Beams of high-energy protons can be precisely targeted and are able to…
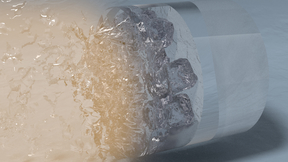
Scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) used giant lasers to flash-freeze water into its exotic superionic phase and record X-ray diffraction patterns to identify its atomic structure for the very first time — all in just a few billionths of a second. The findings are reported today in Nature. In 1988, scientists first predicted that water would…
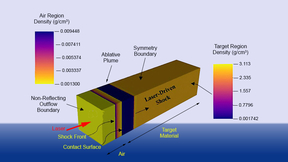
A joint Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL)/Sandia National Laboratories team has commissioned a Line Velocity Interferometer System for Any Reflector (Line VISAR) at Sandia’s Z Machine. Line VISAR is used to measure the velocities of shocks and surface motions when enormous pressures are applied to target materials in high-energy density science experiments…
Physicists designing new laser systems and modeling laser performance at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) now have a powerful new tool in their hands with the Rigel release of Virtual Beam Line++ (VBL++). The current version of VBL, a java-based code, has been in use since 2000. VBL++ has a new architecture using the C++ code and best-in-class standards to…
Using ultrashort laser pulses lasting a few picoseconds (trillionths of a second), Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have discovered an efficient mechanism for laser ablation (material removal) that could help pave the way to the use of lower-energy, less costly lasers in many industrial laser processing applications. The new method, reported in a…
The Laser Institute of America (LIA) has recognized Jamie King, certified laser safety officer (CLSO) at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), with the R. James Rockwell Jr. Educational Achievement Award. The award was presented at the recent International Laser Safety Conference (ILSC), held in Kissimmee, Florida. The award, presented biennially since 2005,…
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team of physicists and target engineers has reached an important goal with a new technique for electroplating copper and gold to create tiny, smoothly spherical inertial confinement fusion (ICF) target shells. The target designers engineered a method that electroplates a 1.5-millimeter plastic capsule as it bobs up and down…
The annual National Ignition Facility (NIF) and Jupiter Laser Facility (JLF) User Group meeting brought together more than 180 researchers to learn about the capabilities, recent experiments and new experimental platforms of both Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) facilities. The attendees included 61 students and represented 31 institutions across six countries…
Advances in deep-learning tools for predictive modeling at NIF and updates on high-power lasers used for fusion research around the world were among the dozens of topics presented at a recent Photonics West conference chaired by leaders in Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's National Ignition Facility & Photon Science (NIF&PS) directorate. The High Power…
For Tom Epperly, writing software is both a lifelong avocation and a hobby. So, working on a major redesign of NIF’s Virtual Beam Line (VBL) code is a dream come true. As the software architect of the VBL++ project, he is part of the team responsible for reimplementing the older Java-based VBL code into C++ so it can run on supercomputers. "The chance to be the software…
High-energy density (HED) science is foundational to the nationally important research conducted by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) — yet few universities offer programs geared for the study of matter and energy under extreme conditions. And even fewer offer such courses for students attending minority-serving institutions. That’s one reason LLNL, Florida A…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's National Ignition Facility (NIF) and General Atomics engineers have created an inertial confinement fusion (ICF) fuel capsule with a 2-micron-diameter fill tube — and along the way, found a solution to a "Bay Bridge"-like dilemma that could have dramatically slowed the process of fabricating NIF capsules. Last month, NIF conducted…
It was a normal morning for design physicist Madison Martin at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). At 7:45 a.m., she settled into her classified workstation with a cup of tea to check the results of a numerical calculation she ran overnight. If the calculations proved correct, the experiment she was designing on the National Ignition Facility (NIF) would deliver…
The laser guide star revolutionized astronomy by revealing large swaths of the sky that had previously been unseen from Earth due to atmospheric distortions. Now astronomy is on the verge of another great leap forward. The Extremely Large Telescope, which is expected to see first light in 2024, will have a 39-meter-diameter primary mirror — more than three times the size…
Daniel Clark, leader of NIF’s Capsule Modeling Working Group within LLNL’s Inertial Confinement Fusion (ICF) Program, has been named the winner of the 2018 Ronald C. Davidson Award for Plasma Physics. The annual award is presented by AIP (American Institute of Physics) Publishing, in collaboration with the American Physical Society (APS) Division of Plasma Physics, to…