Back
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and artificial intelligence (AI) computer company Cerebras Systems have integrated the world’s largest computer chip into the National Nuclear Security Administration’s (NNSA’s) Lassen system, upgrading the top-tier supercomputer with cutting-edge AI technology. Technicians recently completed connecting the Silicon Valley-based…
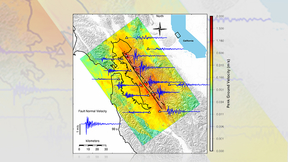
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team has published new supercomputer simulations of a magnitude 7.0 earthquake on the Hayward Fault. This work represents the highest-ever resolution ground motion simulations from such an event on this scale. The study used the SW4 code developed at LLNL. Simulations resolved rapidly varying shaking with broader band…
One of the most common congenital heart defects, coarctation of the aorta (CoA) is a narrowing of the main artery transporting blood from the heart to the rest of the body. It affects more than 1,600 newborns each year in the United States, and can lead to health issues such as hypertension, premature coronary artery disease, aneurysms, stroke and cardiac failure. To…
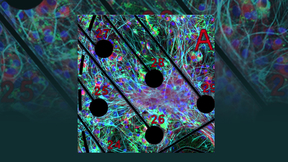
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have increased the complexity of neuronal cultures grown on microelectrode arrays, a key step toward more accurately reproducing the cellular composition of the human brain outside the body. As described in a recently published paper in Scientific Reports, an LLNL team led by biomedical scientist Heather Enright…
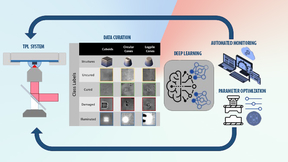
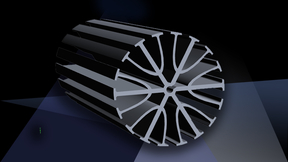
Two-photon lithography (TPL) — a widely used 3D nanoprinting technique that uses laser light to create 3D objects — has shown promise in research applications but has yet to achieve widespread industry acceptance due to limitations on large-scale part production and time-intensive setup. Capable of printing nanoscale features at a very high resolution, TPL uses a laser…
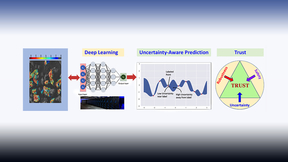
Two papers featuring Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists were accepted in the 2020 International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), one of the world’s premier conferences of its kind. The first, authored by three LLNL researchers, describes a new “mix-n-match” method for calibrating uncertainty of deep learning models. Uncertainty qualification is…
The COVID-19 pandemic and its subsequent restrictions on gatherings and travel have forced institutions and companies around the world to rethink how they offer their summer programs and internships, and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is no exception. This year’s Data Science Challenge with the University of California, Merced, the second such event of its…
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today announced the recipients of the fall 2019 awards for the High Performance Computing for Energy Innovation (HPC4EI) initiative, including four newly funded projects led out of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. The 11 projects selected for a total of $3.3 million in funding under the High Performance Computing for Manufacturing…
To meet the needs of tomorrow’s supercomputers, the National Nuclear Security Administration’s (NNSA’s) Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) has broken ground on its Exascale Computing Facility Modernization (ECFM) project, which will substantially upgrade the mechanical and electrical capabilities of the Livermore Computing Center. The upgrades will enable the…
Surrogate models supported by neural networks can perform as well, and in some ways better, than computationally expensive simulators and could lead to new insights in complicated physics problems such as inertial confinement fusion (ICF), Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists reported. In a paper published by the Proceedings of the National Academy of…
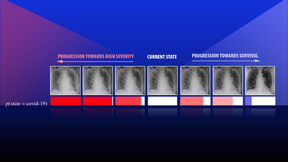
As artificial intelligence (AI) becomes increasingly used for critical applications such as diagnosing and treating diseases, predictions and results regarding medical care that practitioners and patients can trust will require more reliable deep learning models. In a recent preprint (available through Cornell University’s open access website arXiv), a team led by a…
To help accelerate discovery of therapeutic antibodies or antiviral drugs for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) has launched a searchable data portal to share its COVID-19 research with scientists worldwide and the general public. The portal houses a wealth of data LLNL scientists have gathered from their ongoing…
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) today issued the spring 2020 solicitation for the High Performance Computing for Energy Innovation (HPC4EI) Program, aimed at improving manufacturing processes and energy efficiency through supercomputing. Managed by LLNL, the HPC4EI Program provides industry with HPC expertise and…
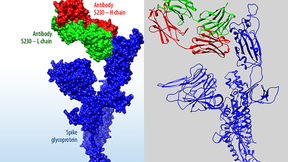
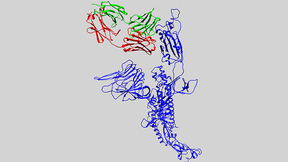
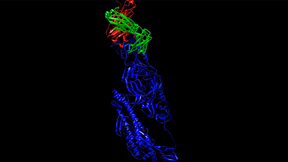
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have identified an initial set of therapeutic antibody sequences, designed in a few weeks using machine learning and supercomputing, aimed at binding and neutralizing SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. The research team is performing experimental testing on the chosen antibody designs. Currently, treating…
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to impact millions of people worldwide, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and its industry partners are committed to applying the nation’s most powerful supercomputers and expertise in computational modeling and data science to battling the deadly disease. To assist in this effort, the Laboratory, Penguin Computing and AMD…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists are contributing to the global fight against COVID-19 by combining artificial intelligence/machine learning, bioinformatics and supercomputing to help discover candidates for new antibodies and pharmaceutical drugs to combat the disease. See the visualization Backed by five high performance computing (HPC) clusters…
The White House announced the launch of the COVID-19 High Performance Computing Consortium to provide COVID-19 researchers worldwide with access to the world’s most powerful high performance computing resources that can significantly advance the pace of scientific discovery in the fight to stop the virus. “America is coming together to fight COVID-19 and that means…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) and Advanced Micro Devices Inc. (AMD) today announced the selection of AMD as the node supplier for El Capitan, projected to be the world’s most powerful supercomputer when it is fully deployed in 2023. With its advanced computing and graphics processing units (CPUs/GPUs), El Capitan’s peak…
A team of computer scientists and mathematicians from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) bested more than two dozen teams to place first overall in Challenge 1 of the Department of Energy’s (DOE) Grid Optimization (GO) Competition, an ongoing series of contests aimed at developing a more reliable, resilient and secure U.S. electrical grid and solving complex…
The future of commuter traffic probably looks something like this: ride-hailing companies operating fleets of autonomous electric vehicles alongside an increasing number of semi-autonomous EVs co-piloted by humans, all supported by a large infrastructure of charging stations. This scenario is particularly likely in California, which has committed to reducing carbon…