Back
The University of Utah has announced the creation of a new oneAPI Center of Excellence focused on developing portable, scalable and performant data compression techniques. The oneAPI Center will be headed out of the University of Utah’s Center for Extreme Data Management Analysis and Visualization (CEDMAV) and will involve the cooperation of Lawrence Livermore National…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) has signed a memorandum of understanding with high performance computing (HPC) facilities in Germany, the United Kingdom and the United States, jointly forming the International Association of Supercomputing Centers (IASC). LLNL and co-founders — the Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC) Hartree Centre, the National…
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team will be among the first researchers to perform work on the world’s first exascale supercomputer — Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Frontier — when they use the system to model cancer-causing protein mutations. Led by Harsh Bhatia, a computer scientist in the Center for Applied Scientific Computing (CASC) at LLNL, the team…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and the rest of the Department of Energy (DOE) national laboratories produce an astronomical amount of data every year. As the volume of data generated from DOE high performance computing (HPC) continues to reach increasing scales of magnitude and new levels of importance for decision-making, where does all this data go and how…
As the U.S. welcomed the world’s first “true” exascale supercomputer, three predecessor machines for Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL) future exascale system El Capitan managed to rank highly on the latest Top500 List of the world’s most powerful supercomputers. Organizers announced the list at the International Supercomputing Conference in Hamburg, Germany…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Amazon Web Services (AWS) have signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) to define the role of leadership-class high performance computing (HPC) in a future where cloud HPC is ubiquitous. Under the MOU, LLNL and AWS will explore software and hardware solutions spanning cloud and on-premises HPC environments, with the goal…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and the United Kingdom’s Hartree Centre are launching a new webinar series intended to spur collaboration with industry through discussions on computational science, high performance computing (HPC) and data science. The first Hartree–Livermore joint webinar on Computational Science (HLCS) takes place May 24, where speakers…
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) today announced the award of an $18 million contract to Cornelis Networks for collaborative research and development in next-generation networking for supercomputing systems at the NNSA laboratories. The Next-Generation High Performance Computing Network (NG-HPCN) project for the NNSA’s…
If a cancer patient tests positive for COVID-19, are they more likely to become hospitalized from the disease? That depends on certain risk factors, according to a new study by researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), who looked to identify cancer-related risks for poor outcomes from COVID-19…
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team has developed a comprehensive dynamic model of COVID-19 disease progression in hospitalized patients, finding that risk factors for complications from the disease are dependent on the patient’s disease state. Using a machine learning algorithm on a dataset of electronic health records (EHRs) from more than 1,300…
The Oppenheimer Science and Energy Leadership Program (OSELP) has selected Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory computer scientist Kathryn Mohror and materials scientist T. Yong Han as 2022 fellows. Established in 2017, OSELP is a distinguished fellowship program that brings together exceptional leaders to explore the complexities, challenges and opportunities facing the…
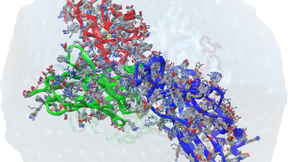
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers and a multi-institutional team of scientists have developed a highly detailed, machine learning-backed multiscale model revealing the importance of lipids to the signaling dynamics of RAS, a family of proteins whose mutations are linked to numerous cancers. Published by the Proceedings of the National Academy of…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) has established the AI Innovation Incubator (AI3), a collaborative hub aimed at uniting experts in artificial intelligence (AI) from LLNL, industry and academia to advance AI for large-scale scientific and commercial applications. LLNL has entered into a new memoranda of understanding with Google, IBM and NVIDIA, with plans to…
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL)-led collaboration targeted at using machine learning to reduce defects and carbon emissions in steelmaking is one of eight new projects receiving Department of Energy (DOE) funding through the High Performance Computing for Manufacturing (HPC4Mfg) Program. DOE’s Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE)…
It was a Supercomputing conference like none other before it. For the first time ever, the 2021 International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis (SC21) went hybrid, with dozens of both in-person and virtual workshops, technical paper presentations, panels, tutorials and “birds of a feather” (BOF) sessions. Under the ongoing specter…
A suite developed by a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team to simplify evaluation of approximation techniques for scientific applications has won the first-ever Best Reproducibility Advancement Award at the 2021 International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis (SC21). Newly instituted by the conference, the award…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) has joined the international Human Vaccines Project (HVP), bringing Lab expertise and computing resources to the consortium to aid development of a universal coronavirus vaccine and improve understanding of immune response. The HVP is a nonprofit, public-private partnership with a mission to decode the human immune system and…
Though the arrival of the exascale supercomputer El Capitan at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is still almost two years away, teams of code developers are busy working on predecessor systems to ensure critical applications are ready for Day One. Delivered in February, the “RZNevada” early-access system is providing experts at the National Nuclear Security…
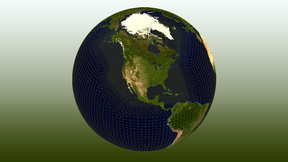
A new version of the Energy Exascale Earth System Model (E3SM) is two times faster than its earlier version released in 2018. Earth system models have weather-scale resolution and use advanced computers to simulate aspects of Earth’s variability and anticipate decadal changes that will critically impact the U.S. energy sector in coming years. Version 2 of the Energy…
The Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration’s (DOE/NNSA’s) Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) announced the awarding of a subcontract to Dell Technologies for additional supercomputing systems to support NNSA’s nuclear deterrent mission. In partnership with Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) and Sandia National Laboratories (SNL), the…