Back
A special issue of the journal Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics was recently released that highlights multiscale modeling and experiments, an area of energetic materials science and technology in which LLNL researchers have played a leading role for some time. The issue features the work of MSD’s Keo Springer, Will Bassett, Sorin Bastea, Svjetlana Stekovic,…
Laboratory materials scientist Aurélien Perron (MSD) was selected to receive the 2020 Young Leaders Professional Development Award from the Functional Materials Division of The Minerals, Metals, and Materials Society (TMS). This award was created to enhance the professional development of dynamic young people from the five technical divisions of TMS by helping them…
Work by PLS scientists Jae-Hyuck Yoo and Andrew Lange (both MSD) and Engineering’s John Chesser, Steve Falabella, and Selim Elhadj was recently highlighted in Physica Status Solidi A: Applications and Materials Science as the November 2019 cover story. The research described in the article explores guidelines for designing materials with high laser damage lifetimes. To…
Laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) is a method of additive manufacturing characterized by the rapid scanning of a high-powered laser over a thin bed of metallic powder to create a single layer, which may then be built upon to form larger structures. Most melting, resolidification, and subsequent cooling take place at higher rates and with higher thermal gradients than in…
Livermore’s Joel Berry (MSD) has coauthored a pair of papers describing promising methods for controlling the structure and properties of 2D materials. In one paper, Berry and his colleagues at the University of Pennsylvania and University of Chicago propose a new atomic-scale approach to form nano- to macro-patterned thin films with tailored properties (mechanical,…
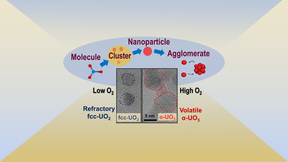
The predictive models that describe the fate and transport of radioactive materials in the atmosphere following a nuclear incident (explosion or reactor accident) assume that uranium-bearing particulates would attain chemical equilibrium during vapor condensation. In a new study, funded by the Office of Defense Nuclear Nonproliferation Research and Development (DNN R&D…
Officials from the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) gathered with elected leaders and industry professionals recently to dedicate and tour the Advanced Manufacturing Laboratory, a new collaborative hub intended to spur public-private partnerships. The $10 million, 14,000-square-foot facility, located in the…
Driven by the success of machine learning (ML) in commercial applications such as product recommendations and advertising, researchers are attempting to apply ML tools to scientific data analyzation. One such application area is materials science, where ML methods could accelerate the selection, development, and discovery of materials by learning structure–property…
Former Secretary of Energy Rick Perry recognized Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) staff with six Secretary’s Honor Awards at a ceremony at Department of Energy (DOE) headquarters. The Secretary’s Honor Awards are bestowed on teams that have achieved a singular accomplishment that demonstrates a high level of performance and dedication to public service. As his…
At first glance it might be mistaken for a model of the Millennium Falcon of “Star Wars” fame. But it’s actually a new radiation-effects diagnostic that triples the number of material samples that can be exposed to X-rays in a single NIF shot. Designed by researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Sandia National Laboratories, the STAR (Sample Test…
On October 29, 2019, twelve Lawrence Livermore postdocs took to the stage, each with three slides and three minutes to answer the question: “Why is your research important?” The presentations, part of a yearly competition known as the Research Slam!, were a culmination of months of development, training, and practice. The 2019 program kicked off with seminars about…
This fall, the American Nuclear Society is publishing the second edition of the Plutonium Handbook, a 4000-page, 7-volume compendium that delivers a comprehensive review of plutonium chemistry. (The first edition was published 50 years ago.) Five years in the making, this publication includes contributions from 17 Lawrence Livermore researchers, two of whom are also on the…
Approximately 1000 students came to the Laboratory this summer to engage in work-study employment in science, technology, engineering, mathematics, and administrative fields. PLS hosted a number of these students through its summer student programs (described below). Nuclear science and security The Glenn T. Seaborg Institute hosted 12 students this summer, including 8…
While 3D printing at the nanoscale — producing intricate features orders of magnitude smaller than the width of a human hair — has significant potential in industry and commercial applications, wide adoption has been impractical because of the slow speed and low throughput of the most widely used nanoprinting technique, two-photon lithography (TPL). But in the latest issue…
Lawrence Livermore researchers and collaborators at the University of Texas at El Paso have developed a concept that allows the integration of the characteristic properties of fullerene in 3D graphene networks. In the study, the team optimized the interaction between 3D graphene networks and fullerenes, specifically in the context of stability and charge transfer in an…
Drastic changes in climate and global losses in biodiversity are increasing the need to shift the incumbent energy and chemical infrastructure from a fossil-fuel based system to a sustainable-energy based system. Such a system will require that the production of fuels and chemicals use only sustainable energy (e.g., solar) and simple, abundant feedstocks like carbon…
Astrophysics is a growth area in the Laboratory’s advancement of basic science for national and global security needs. In this field, data science helps researchers catalog and interpret objects orbiting Earth and process huge volumes of data captured by ground- and space-based telescopes.
A new generation of ultra-low-density (less than 20 milligrams per cubic centimeter) metal foams for laser targets has been made from metal nanowire suspensions via a unique freeze-casting process. In order to optimize the density, geometry, composition, and mechanical properties of these metal foams, it is necessary to develop nanowire stock materials of highly controlled…
A new publication in the journal Advances in Physics by three Laboratory researchers describes plutonium from first-principles theory. This is the first time a first-principles explanation for the perplexing anomalous negative thermal expansion of the delta phase of plutonium has been reported. Per Söderlind, Alex Landa, and Babak Sadigh (all PHYS) reviewed developments in…
Multilayer interference mirrors are enabling components in x-ray optical systems. These mirrors consist of periodic or non-periodic structures of alternating thin film layers of two or more materials deposited on an optical substrate. Today’s applications and experimental facilities (including the National Ignition Facility) require novel, multilayer-based hard x-ray…













![ACS journal cover of [60]fullerene monoadduct physisorbed on a graphene network](https://contenthub.llnl.gov/sites/contenthub/files/styles/scaled_16_9_ratio_at_288x162/public/2022-02/2019-08-27_applied-materials-cover.jpg?itok=I48wP8px)