Back
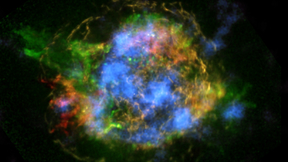
For the first time, an international team of astrophysicists, including Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory scientists, have unraveled how stars blow up in supernova explosions. Using NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR ) -- a high-energy X-ray observatory -- the international collaboration created the first-ever map of radioactive material in a…
Tularemia is endemic in the northeastern United States, and is considered to be a risk to biosecurity -- much like anthrax or smallpox -- because it has already been weaponized in various regions of the world. At the 58th Annual Biophysical Society Meeting, which started Saturday and continues through Wednesday in San Francisco, Geoffrey Feld, a postdoctoral researcher in…
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory physicist and his colleagues have found a new application for the tools and mathematics typically used in physics to help solve problems in biology.Specifically, the team used statistical mechanics and mathematical modeling to shed light on something known as epigenetic memory -- how an organism can create a biological memory of…
LIVERMORE, Calif. - Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientist Steve Payne was recently selected as a fellow of SPIE, an international professional society for optics and photonics. Payne, an active SPIE participant since the mid-1980s, is the group leader for sensor materials and measurements in the Lab's Materials Sciences Division and is the associate…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers have begun to develop a technique that provides a practical approach for looking into the complex physical and chemical processes that occur during fallout formation following a nuclear detonation. Post-detonation nuclear forensics relies on advanced analytical techniques and an understanding of the physio-chemical…
Patrice Turchi, a Distinguished Member of the Technical Staff at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, will be installed as the 2014 vice president of The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society (TMS) in February.Turchi, who is the group leader of LLNL's Materials Science Division of the Physical and Life Sciences Directorate, will assume his new role at TMS during the…
How well do you know science? Do you know it well enough to explain it to a fellow scientist, engineer or your boss? What about a news reporter, college or high school student? Or, the ultimate challenge, a fifth-grade student? That is what the Flame Challenge is all about: encouraging scientists to voluntarily create ways to communicate complex material simply, clearly…
Space weathering, which works similar to geological erosion on the Earth, produces water in the rims of tiny particles of interplanetary dust. The discovery may have implications on the origins of life and sources of water throughout the galaxy. As a byproduct of star formation, water ice is the most abundant solid material in the universe. But this new source was a…
A team of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory scientists are using mini-satellites that work as "space cops" to help control traffic in space. The scientists used a series of six images over a 60-hour period taken from a ground-based satellite to prove that it is possible to refine the orbit of another satellite in low earth orbit."Eventually our satellite will be…
In an effort to put to good use natural gas (methane) that might otherwise become pollution, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is collaborating with start-up company Calysta Energy on a new technology to convert natural gas to liquid fuel.The process involves taking natural gas from oil and gas operations, and converting it to methanol that can be used as a fuel or…
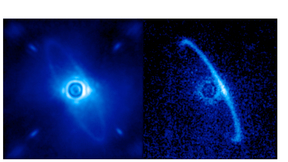
After nearly a decade of development, construction and testing, the world's most advanced instrument for directly imaging and analyzing planets orbiting around other stars is pointing skyward and collecting light from distant worlds."Even these early first-light images are almost a factor of 10 better than the previous generation of instruments. In one minute, we were…
A Livermore team led by Félicie Albert, along with researchers from the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA) and SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, has produced x-ray pulses with all the characteristics users desire, with the added benefit of being generated on a system the size of a large tabletop.
LIVERMORE, Calif. - Four Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory scientists have been selected as 2013 fellows of the American Physical Society (APS). Physicist Charles Cerjan was cited by the Division of Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics for "seminal contributions to time-dependent Schrodinger equation propagation algorithms and their application to particle scattering…
Sometimes you have to apply a little pressure to get magnetic materials to reveal their secrets. By placing a permanent magnet under high pressures, Lawrence Livermore researchers are exploring how atomic structure enhances magnetic strength and resistance to demagnetization. This fundamental research into magnetic behavior has important implications for engineering…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's (LLNL) Ken Moody has been awarded the distinction of fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). Election as a fellow is an honor bestowed upon AAAS members by their peers to recognize distinguished efforts to advance science or its applications. This year, AAAS awarded 388 members with this honor…
Using deep sea corals gathered near the Hawaiian Islands, a Lawrence Livermore scientist, in collaboration with UC Santa Cruz colleagues, has determined that a long-term shift in nitrogen content in the Pacific Ocean has occurred as a result of climate change. Overall nitrogen fixation in the North Pacific Ocean has increased by about 20 percent since the mid 1800s -- a…
SAN FRANCISCO - Researchers are developing a new kind of geothermal power plant that will lock away unwanted carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) underground and use it as a tool to boost electric power generation by at least 10 times compared to conventional geothermal power. The technology for this design already exists in different industries, and the researchers, led by Tom Buscheck…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers have combined ultrafast time-resolved experimental measurements with theory to reveal how an explosive responds to a high-impact shock.The work involved advances in both ultrafast experimental shock wave methods and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation techniques, and the combination of experiment and simulation is a…
That supernova, caused from the cataclysmic death of a star, could have even triggered the birth of the sun.Most of the mass in the universe is from light elements like hydrogen and helium. The heavier elements that make up planets are produced inside stars or created when they explode as supernovae. But according to researchers, it is unclear how such events may have…
This is the first Science and Technology Center grant UB has received. With the grant, UB and its partner institutions will establish the Biology with X-ray Free Electron Lasers (BioXFEL) research center, headquartered in Buffalo. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is a partner institution of the BioXFEL center.The BioXFEL (pronounced bio-x-fell) center will…