Back
A chemist who is the director of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL) Forensic Science Center is the recipient of the 2020 “Outstanding Early Career Achievement in Forensic Science Award.” The award, given to LLNL’s Audrey Williams, is presented annually by the American Academy of Forensic Sciences (AAFS) Past Presidents Council. This year’s award will be…
Former Secretary of Energy Rick Perry recognized Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) staff with six Secretary’s Honor Awards at a ceremony at Department of Energy (DOE) headquarters. The Secretary’s Honor Awards are bestowed on teams that have achieved a singular accomplishment that demonstrates a high level of performance and dedication to public service. As his…
On October 29, 2019, twelve Lawrence Livermore postdocs took to the stage, each with three slides and three minutes to answer the question: “Why is your research important?” The presentations, part of a yearly competition known as the Research Slam!, were a culmination of months of development, training, and practice. The 2019 program kicked off with seminars about…
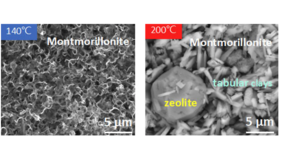
The migration of low levels of plutonium has been observed at the Nevada National Security Site (NNSS) and attributed to colloid-facilitated transport. (A colloid is a mixture in which one substance of microscopically dispersed particles is suspended throughout another substance.) To understand why plutonium is migrating, LLNL scientists performed experiments using mineral…
This fall, the American Nuclear Society is publishing the second edition of the Plutonium Handbook, a 4000-page, 7-volume compendium that delivers a comprehensive review of plutonium chemistry. (The first edition was published 50 years ago.) Five years in the making, this publication includes contributions from 17 Lawrence Livermore researchers, two of whom are also on the…
Approximately 1000 students came to the Laboratory this summer to engage in work-study employment in science, technology, engineering, mathematics, and administrative fields. PLS hosted a number of these students through its summer student programs (described below). Nuclear science and security The Glenn T. Seaborg Institute hosted 12 students this summer, including 8…
Human hair is invaluable to forensic investigations because it is one of the few biological specimen types that persist for long periods of time. However, hair contains minimal intact nuclear DNA, leading researchers to search for alternate identification methods using hair. Previous research led to a new protein-based identification technique, providing a way to identify…
The probability that a nucleus will absorb a neutron is important to many areas of nuclear science, including the production of elements in the cosmos, reactor performance, nuclear medicine and defense applications. New research from a team led by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists reveals that the radioactive isotope zirconium-88 (⁸⁸Zr) is 100,000…
Jason Brodsky says his work is like “looking for a candle in a raging inferno.” But the Lawrence Livermore physicist believes finding that “candle” could be the key to understanding existence itself. Brodsky’s specialty is rare-event detection, both during his Princeton graduate work on dark matter and his current postdoctoral research at LLNL, in which he searches for…
Nuclear emergency teams, safeguards specialists and others may one day benefit from an expanded nuclear fission chain theory and detectors developed by a team of Lawrence Livermore Nationla Laboratory (LLNL) physicists. The Livermore scientists have bolstered their theory for understanding nuclear fission chains -- a cascade of atomic nuclei splitting, each initiated by a…
Like a game of "hide and seek," Lawrence Livermore astrophysicists know that there are black holes hiding in the Milky Way, just not where. If they find them toward the galactic bulge (a tightly packed group of stars) and the Magellanic Clouds, then black holes as massive as 10,000 times the mass of the sun might make up dark matter. If they are only toward the galactic…
The program to extend the life of the W80 nuclear warhead recently achieved a significant milestone when the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) gave passing grades to the plans to refurbish certain components and the proposed approach to developing component cost estimates. Passing the milestone confirms that the life extension program (LEP), dubbed the W80-4…
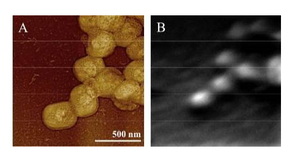
Because of their size, lack of symmetry, structural heterogeneity, and high molecular weight, most large animal and human viruses are not amenable to typical analytical techniques, such as x-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance analyses, or fine-scale reconstruction by cryo-electron microscopy. In a recently published paper in Analytical Chemistry, NACS and BBTD…
Ecological research focuses on understanding how population-level dynamics—such as the growth rate of a particular population of microbes—contribute to ecosystem-level processes. Ecosystem scientists researching climate change often study the role of microbes in the carbon cycle, for example, so knowing how quickly they grow is a fundamental metric to reaching that…
During their 15 years as a certified laboratory for the Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), a score of LLNL chemists have developed some first-rate habits. One of them is earning “A” grades on the organization’s environmental proficiency tests. In recently-announced results, LLNL earned its eighth straight “A” grade during last fall’s OPCW…
Our researchers and collaborators created a technique used to determine the shape of a neutron-rich ruthenium isotope.
On Sept. 7, 2017, 12 postdoc finalists of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's 2017 Research Slam! talked for three minutes each about their work before a distinguished panel of judges. The postdocs were competing for monetary prizes of two, three and four thousand dollars for third, second and first place winners, but perhaps the biggest prize was the chance to…
Materials scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have developed a novel experimental method to access the dynamic regime of radiation damage formation in nuclear and electronic materials. Their approach is based on using pulsed ion beams for measurements of defect lifetimes, interaction rates and diffusion lengths. The creation of stable radiation…
Mavrik Zavarin has been named the new Director of The Glenn T. Seaborg Institute (GTSI) in the Physical & Life Sciences Directorate. In this capacity, Mavrik will continue to develop the GTSI's mission to carry out cutting-edge research in areas key to LLNL's Nuclear Security and Energy & Environment mission areas, with an emphasis on providing opportunities for…
Fans of the popular TV series "CSI" know that the forensics experts who investigate crime scenes are looking for answers to three key questions: "Who did it; how did they do it; and can we stop them from doing it again?"The field of nuclear forensics, an important element of LLNL’s national security mission, has similar goals and uses similar techniques — but with even…