Back
After decades of fusion research, a burning plasma state was achieved on November 2020 and February 2021 at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s National Ignition Facility (NIF), the world’s most energetic laser. Obtaining a burning plasma is a critical step toward self-sustaining fusion energy. A burning plasma is one in which the fusion reactions themselves are the…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL) Christopher Stolz has been elected as a fellow of SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics. Stolz, an associate program manager in charge of the National Ignition Facility (NIF) optics supply, has worked at LLNL in the laser directorate as a thin film engineer for more than 30 years; first in AVLIS and then…
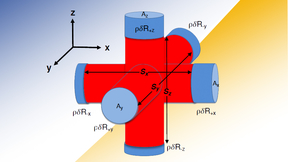
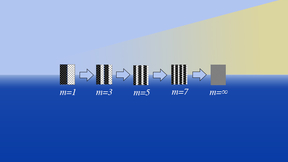
New research conducted at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) explores the expansion of a classical mechanics model, which has been useful for understanding asymmetries in inertial confinement fusion (ICF) implosions, from a two-piston to a six-piston model to capture higher-mode asymmetries. The work is featured in the Physics of Plasmas. LLNL authors included…
The discovery of more than 4,500 extra-solar planets has created a need for modelling their interior structure and dynamics. As it turns out, iron plays a key role. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and collaborators have used lasers at the National Ignition Facility to experimentally determine the high-pressure melting curve and structural…
Omar Hurricane, chief scientist for the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory inertial confinement fusion (ICF) program, is a recipient of the 2021 Edward Teller Award. The Fusion Energy Division of the American Nuclear Society (ANS) presented the award to Hurricane for his “visionary scientific insights and leadership of National Ignition Facility (NIF) experiments…
Research conducted at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is taking a closer look at entropy — the measure of internal energy per unit temperature that is unavailable for doing useful work — in experiments at the National Ignition Facility (NIF). Work by LLNL physicist Peter Amendt is highlighted as an Editor’s Pick in Physics of Plasma, showing that an added…
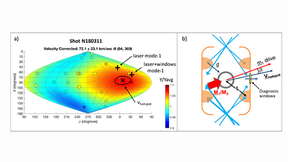
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers now have a better understanding on how strong the magnetic fields are in an inertial confinement fusion (ICF) implosion at the National Ignition Facility (NIF), the world’s most energetic laser. The researchers described their findings a paper published in Physics of Plasmas with LLNL scientists Chris Walsh serving…
Three Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) physicists have been selected as 2021 fellows of the American Physical Society (APS). The new fellows represent a selection of physics expertise, ranging from intense laser-matter interactions and inertial fusion energy science to leading the development of edge simulation models and codes to pioneering new regimes of…
When Daniel Martin put the finishing touches on an autonomous vehicle robot, complete with an ultrasonic sensor to detect and evade obstacles, he knew he wanted to become an engineer. A high school student at the time, he was fascinated by the design and functionality of robots. Fast forward several years, and Martin is now a second-year electrical engineering Ph.D…
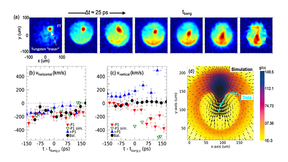
The experimental observations of high-velocity particle-laden flow interactions has been sparse, given the difficulty of generating high-velocity flows of many particles. These observations play an important role in understanding a wide range of natural phenomena, ranging from planetary formation to cloud interactions. That is, until now. In experiments conducted at the…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and engineers have posted another banner year securing major grants through the Department of Energy’s (DOE) Technology Commercialization Fund (TCF). “I think the Laboratory did very well again, reflecting a variety of types and approaches to our research and development projects,” said Rich Rankin, the director of…
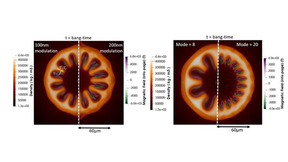
Imagine having a balloon between both hands and trying to squeeze it with the same force on all sides so that it uniformly shrinks down. However, if you push on one side harder than the other the balloon won’t compress uniformly and will, in fact, move away from the hand that is pushing harder. The same thing happens when the drive pushing on an inertial confinement fusion…
While laser-based 3D printing techniques have revolutionized the production of metal parts by greatly expanding design complexity, the laser beams traditionally used in metal printing have drawbacks that can lead to defects and poor mechanical performance. Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) are addressing the issue by exploring alternative shapes…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists are working on a new diagnostic capability that will provide, for the first time, the ability to make X-ray radiographic movies. The first experiment testing the principle, dubbed the Bipolar Reset Experiment (BIRX), was conducted at LLNL’s Flash X-Ray (FXR) deep-penetration radiographic facility at Site 300. The…
On Aug. 8, 2021, an experiment at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL’s) National Ignition Facility (NIF) made a significant step toward ignition, achieving a yield of more than 1.3 megajoules (MJ). This advancement puts researchers at the threshold of fusion ignition, an important goal of the NIF, and opens access to a new experimental regime. The experiment…
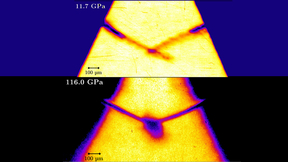
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have explored high-pressure behavior of shock-compressed tantalum at the Omega Laser Facility at the University of Rochester’s Laboratory for Laser Energetics (LLE). The work showed tantalum did not follow the predicted phase changes at high pressure and instead maintained the body-centered cubic (BCC) phase until…
The Fusion Power Associates (FPA) Board of Directors has selected Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) experimental physicist Tammy Ma as the recipient of its 2021 Excellence in Fusion Engineering Award. She will receive the award at the Fusion Power Associates 42nd annual meeting Dec. 15-16 in Washington, D.C. Click here for a complete list of previous recipients…
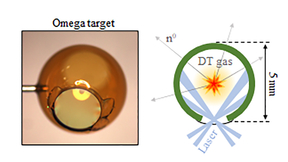
Scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and the Laboratory for Laser Energetics (LLE) have described a simple 3D model in hohlraums and capsules for inertial confinement fusion (ICF) implosions. The model will assist in delivering the required implosion symmetry on layered deuterium-tritium (DT) implosions for ignition. The results of the work remove…
The last U.S. underground nuclear explosive tests, which were key to assessing the design and viability of the country’s nuclear weapons, occurred over 27 years ago. However, the need for deeper understanding of the complex physical processes that drive nuclear weapon performance and for putting stockpile design and assessment on a solid science-based foundation continue…
The National Ignition Facility (NIF) at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) has added a new tool to its growing list of capabilities. A team of scientists has demonstrated a new geometry for a neutron source platform for NIF, called the inverted-corona platform, which does not rely on spherically symmetric laser irradiation. This new tool has significantly less…