Back
Félicie Albert, staff scientist at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's (LLNL) NIF & Photon Science and the Joint High Energy Density Sciences organization, has been elected a Kavli Fellow of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences (NAS). As a new Kavli Fellow, Albert was invited to present a poster about next-generation X-ray light sources during NAS’ annual Kavli…
Data correlating two factors that lead to implosion asymmetries have brought Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists a step closer to understanding the gap between simulations and performance of inertial confinement fusion (ICF) experiments at the National Ignition Facility (NIF). These experiments aim to ignite a propagating fusion burn wave in deuterium…
High energy density (HED) scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have helped launch a new National Science Foundation (NSF) effort to understand the physical and astrophysical properties of matter under pressures strong enough to change the structure of individual atoms. The Center for Matter at Atomic Pressures (CMAP) is hosted by the University of…
SPIE, the International Society for Optics and Photonics, recently announced the election of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) research engineer Richard Leach as a senior member of the organization. SPIE recognizes senior members based on exceptional professional experience, active involvement with the optics community and/or significant performance that sets…
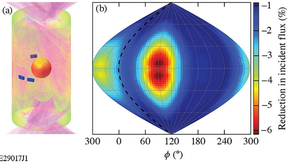
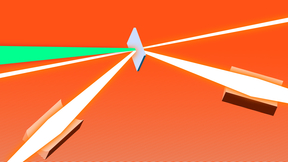
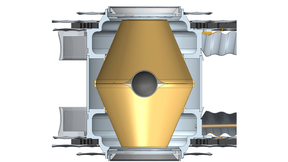
Initial NIF experiments using a full-scale version of the Frustraum hohlraum have produced nearly round inertial confinement fusion (ICF) implosions and more laser-induced energy absorption by the fuel-filled capsule. National Ignition Facility (NIF) researchers are optimistic that results from the initial tests of the novel angular-shaped hohlraum could create more…
Using the power of the National Ignition Facility (NIF), the world’s highest-energy laser system, researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and an international team of collaborators have developed an experimental capability for measuring the basic properties of matter, such as the equation of state (EOS), at the highest pressures thus far achieved in a…
Three scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) are recipients of the 2020 John Dawson Award for Excellence in Plasma Physics Research from the American Physical Society. The honor recognizes a particular recent outstanding achievement in plasma physics research. Hye-Sook Park, Steven Ross and Dmitri Ryutov are part of an international team of…
There are giants among us — gas and ice giants, to be specific. They orbit the same star, but their environmental conditions and chemical makeup are wildly different from those of Earth. These enormous planets — Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune and Uranus — can be seen as natural laboratories for the physics of matter at extreme temperatures and pressures. Now, an international…
Surrogate models supported by neural networks can perform as well, and in some ways better, than computationally expensive simulators and could lead to new insights in complicated physics problems such as inertial confinement fusion (ICF), Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists reported. In a paper published by the Proceedings of the National Academy of…
In a paper recently published by Physical Review Letters, a team of researchers including scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) detail the first quantitative measurements of the magnetic field structure of plasma filamentation driven by the Weibel instability, using a novel optical Thompson scattering technique. These experiments study the processes…
When stars explode as supernovae, they produce shock waves so powerful they can blast streams of particles called cosmic rays into the universe at nearly the speed of light. Yet the exact mechanisms behind these phenomena remained mysteries for decades. Now, in experiments at the National Ignition Facility (NIF), an international team of scientists from institutions…
When scientists saw the results from the first-ever Discovery Science experiment on the National Ignition Facility’s (NIF) Advanced Radiographic Capability (ARC) laser, they were genuinely surprised: The experiment produced much higher energy electrons than predicted based on the laser energy and power used on these shots. Those results, which were not typical of new…
At its peak, a NIF inertial confinement fusion (ICF) implosion lasts about 100 trillionths of a second. The imploded fuel is a hundred millionths of a meter in diameter and as much as eight times denser than lead. The center of the imploded capsule is a few times hotter than the core of the sun. Developing a clear understanding of exactly what’s happening in a NIF…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists have employed compound parabolic targets to achieve relativistic effects associated with significantly greater laser intensities. This innovation has substantially expanded the experimental capabilities of the National Ignition Facility’s (NIF) Advanced Radiographic Capability (ARC) laser. The targets, called…
If copper was found in the core of Saturn it would have the same crystalline structure as the copper pipes found in many homes, according to new research from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Johns Hopkins University. In a paper published today by Physical Review Letters, the research team reveals that copper maintains its crystalline structure at…
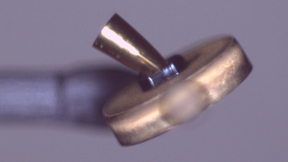
At first glance it might be mistaken for a model of the Millennium Falcon of “Star Wars” fame. But it’s actually a new radiation-effects diagnostic that triples the number of material samples that can be exposed to X-rays in a single NIF shot. Designed by researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Sandia National Laboratories, the STAR (Sample Test…
Ongoing experiments on the sun’s nucleosynthesis (element creation) processes and an update on progress toward achieving ignition were among the dozen invited talks about NIF-related research at the American Physical Society plasma physics conference this fall. The talks, which highlight the importance of NIF & Photon Science Directorate research, drew widespread…
Hohlraums shaped like cylinders have been the workhorse of inertial confinement fusion (ICF) research for three decades. But now an angular hohlraum named “Frustraum” could become a key to the next stages of ICF research at the National Ignition Facility. The LLNL-designed Frustraum could enable a significant boost in the amount of laser-induced energy absorbed…
It’s been more than 10 years since John Ruiz, a mechanical designer in the National Ignition Facility’s (NIF) Facilities and Infrastructure Systems group, left the Army. But last summer, he found himself transported back to one of the most harrowing days of his Army career at the Medal of Honor ceremony for his former squad leader, Staff Sgt. David G. Bellavia. Ruiz was a…
In a new paper published as an “Editors’ Suggestion” in Physical Review Letters, a team of researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory has demonstrated that lead — a metal so soft that it is difficult to machine at ambient conditions — responds similarly to other much stronger metals when rapidly compressed at high pressure. The paper also was highlighted by a …