Back
Using the same baking soda found in most grocery stores, Lawrence Livermore scientists, along with colleagues from Harvard University and the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, have created a significant advance in carbon dioxide capture.The team developed a new type of carbon capture media composed of core-shell microcapsules, which consist of a highly permeable…
Three Lawrence Livermore researchers have received the Department of Energy's 2014 Hydrogen Production R&D Award for developing a system that uses sunlight to split water molecules, producing hydrogen. Shared with collaborators from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL)and the University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV), the award recognizes the team for its work…
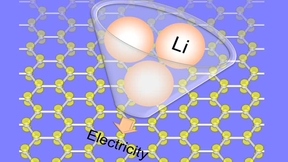
Your cell phone may stay charged longer due to advances in modeling lithium-ion battery storage capacity.New research indicates that lithium-ion batteries could benefit from a theoretical model created at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and Rice University that predicts how carbon components will perform as electrodes.The growing demand for energy storage emphasizes…
Lawrence Livermore scientists are working on a project that will use particles considerably smaller than the size of a human hair to improve the storage capacity of hydrogen-powered vehicles.Using $1.2 million from the Department of Energy's Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE) over three years, LLNL scientist Brandon Wood said that through theory and…
Livermore microbiologist Yongqin Jiao is midway through a five-year study to investigate how certain aerobic bacteria interact with uranium in aquatic environments.