Back
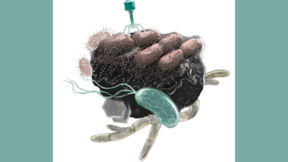
The development of new antibiotics has stalled — new strategies are needed as the world enters the age of antibiotic resistance. To combat this challenge, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists have found that synthetic antibacterial minerals exhibit potent antibacterial activity against topical MRSA infections and increase the rate of wound closure…
Soil is a highly complex microbial habitat that is home to tens of millions of microbial populations, where biotic and abiotic factors shape microbial community structure. Moments of acute pressure on a community, such as rapid environmental changes or fluxes in resource availability, drive successional trajectories that result in altered community structures. One such…
Iron is one of the world’s most abundant elements and a primary component of the Earth's core. Understanding the behavior of iron under extreme conditions, such as ultra-high pressures and temperatures, has implications for the science of geology and the Earth’s evolution. In a study conducted by a team led by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. researchers combined…
PLS staff physicists Ben Zhu and Veronika Kruse were selected by the American Physical Society (APS) as Career Mentoring Fellows for 2023-2024. Ben belongs to PLS’s Fusion Sciences program and Veronika is in the High Energy Density Science section. Part of their duties involve attending selected APS conferences such as the Division of Plasma Physics (DPP) meeting,…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers, along with scientists from more than a dozen institutions, have completed a first-of-its-kind high-resolution assessment of carbon dioxide (CO2) removal (CDR) in the United States. The report, “Roads to Removal: Options for Carbon Dioxide Removal in the United States,” charts a path for the United States to achieve…
A new satellite called XRISM (X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission, pronounced “crism”) was successfully launched from the Tanegashima Space Center in Japan on Sep. 7, 2023. XRISM is a collaboration between the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), with European Space Agency participation, to study extreme…
Geophysicist Christina “Chris” Morency’s research has led her around the globe to demystify the world beneath our feet. Since arriving at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) in 2011, she has held leadership roles on numerous research teams and has worked diligently to make Lawrence Livermore a welcoming place for all. Originally from France, Morency said she is …
The crowds returned to SC, and with them came a renewed excitement for the future of high performance computing (HPC). A record number of attendees — more than 14,000 — experts, researchers, vendors and enthusiasts in the field of HPC descended on the Mile High City for the 2023 International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis,…
Gathered in the Congressional Auditorium on Wednesday, Nov. 15, 17 early-career researchers used three minutes and a single slide to present their pioneering research during the inaugural National Lab Research SLAM. Representing each of the 17 Department of Energy (DOE) national laboratories, finalists presented in four research categories: Energy Security, National…
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL)-led effort that performed an unprecedented global climate model simulation on the world’s first exascale supercomputer has won the first-ever Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) Gordon Bell Prize for Climate Modelling, ACM officials announced Thursday. The Simple Cloud Resolving E3SM Atmosphere Model (SCREAM) team, led…
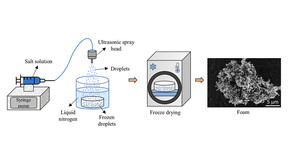
Rising global temperatures are creating an increased demand for cooling as the number of air-conditioning units used worldwide is expected to triple by 2050. However, with 13% of the global population without access to electricity, solutions that can provide cooling without electricity are needed. In a study published in Materials Horizon, a Lawrence Livermore National…
Understanding laser material interactions has applications that include inertial confinement fusion, material research and equation of state studies. Laser ablation, and specifically increasing the pressure that can be achieved from a laser system, is a longstanding topic of scientific research with implications ranging from damage in layered devices like solar cells and…
In new experiments at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s National Ignition Facility, scientists measured the extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) of copper to probe its temperature under extreme pressure. The research appears in the journal Nature Communications. Dynamic compression experiments at high-energy-density laser facilities have expanded the…
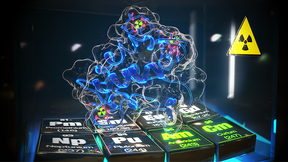
Past and present nuclear activities (energy, research and weapon tests) have increased the need to understand the behavior of radioactive materials in the environment. Nuclear wastes containing actinides (such as plutonium, americium, curium and neptunium) are particularly problematic as they remain radioactive and toxic for thousands of years. However, when compared to…
While neutrinos are one of the most common particles in the universe, their elusive nature makes it challenging to understand their behavior. In new research from the Precision Reactor Oscillation and Spectrum (PROSPECT) Experiment, scientists have produced final results from measurements of neutrinos emitted by a nuclear reactor at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Their…
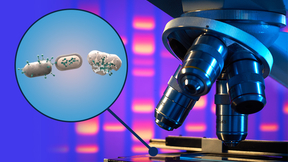
Beneath the Earth's surface, a relentless conflict unfolds as soil viruses prey on their tiny microbial hosts, fundamentally shaping our planet's ecosystems. New research from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and their collaborators at the University of California, Berkeley illuminates a fascinating phenomenon: the demise of soil bacteria and other…
For the second consecutive year, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) hosted a group of student scholars and faculty members from Historically Black Colleges and Universities (HBCUs) on a recent five-day visit. LLNL’s goal is to develop the next wave of summer interns — and to build a strong pipeline of talent — from historically marginalized groups in science,…
The groundbreaking discoveries and scientific advancements that take place at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and across the broader national laboratory system rely on the passage of information from tenured staff scientists to new interns and early career scientists. This past summer, Zachary (Zach) Murphy, a Ph.D. student studying chemistry at the…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory staff scientist Jeremy Feaster has been named as one of the American Institute for Chemical Engineering’s (AIChE) “35 Under 35” award winners for 2023. The recognition honors chemical engineers under the age of 35 who have made outstanding contributions to their field and to the chemical engineering community, according to the…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists Manyalibo “Ibo” Matthews and Frank Graziani have been named 2023 American Physical Society (APS) fellows. Matthews was selected from the Forum in Industrial and Applied Physics unit “for pioneering research in optimizing metal 3D printing and laser materials processing.” Frank Graziani was chosen from the Division of…