Back
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) will partner with outside institutions to improve diversity in the STEM workforce and provide training to underrepresented students and researchers under a pair of projects recently funded by the Department of Energy. With support from DOE’s Funding for Accelerated, Inclusive Research (FAIR) initiative, LLNL will partner with…
Alex Li, a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) summer student in the Computational Chemistry and Materials Science Summer Institute, recently led a study published in the journal Matter to investigate the evolution of plasticity in diamond along different loading orientations and the effects that voids (pores) within the material can have on stresses within the…
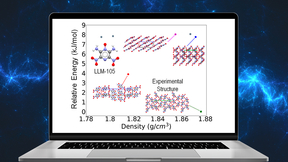
New research by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers and collaborators from Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) demonstrates that crystal structure prediction is a useful tool for studying the various ways the molecules can pack together, also known as ubiquitous polymorphism, in energetic materials. The research also shows promise of becoming an integral part…
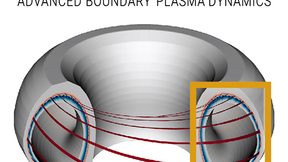
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory-led project aimed at using computing tools to improve understanding of fusion plasma dynamics was among 12 projects recently awarded funding by the Department of Energy (DOE) to accelerate fusion power plant development. The four-year, multi-institutional Advanced Boundary Plasma Dynamics (ABOUND) project will receive $9.25 million…
Scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) collaborated with University of California San Diego (UCSD) to design, assemble, and field a portable optical Thomson scattering diagnostic system for the Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E) — a Department of Energy agency which supports private companies that are developing new ways to generate,…
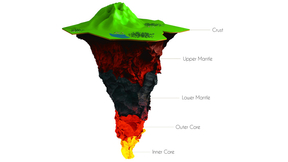
Iron monoxide (FeO), also known as wüstite in its mineral form, is a significant (even if not predominant) component of Earth’s core and the deep interior of Earth and other planets. Most notably, FeO exhibits a richness of condensed-matter phenomena, including crystal-structural phase transformations and melting, electronic transitions, and spin-state transitions that…
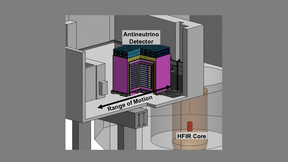
Nuclear reactors, among the brightest terrestrial emitters of antineutrinos, have been central to neutrino physics. For more than a decade, physicists have puzzled over anomalous differences between measurements and predictions of the antineutrino emissions from nuclear reactors. These differences could reveal deficiencies in prediction methods and their underlying nuclear…
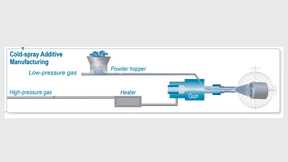
Permanent magnets form the backbone of clean energy technologies from direct-drive wind turbines to electric motors, and will form a key component of the upcoming transition to a green economy. There is significant interest in the application of additive manufacturing approaches to produce permanent magnets, with techniques such as laser powder-bed fusion and binder-jet…
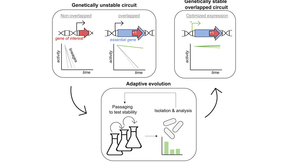
For the past several decades, synthetic biologists have sought to genetically engineer microorganisms for a wide range of application—including therapeutics discovery and delivery, drug manufacturing, agricultural yields, biofuel production, mineral extraction, and waste degradation. This is achieved through the design of genetic circuits, which are made up of DNA parts…
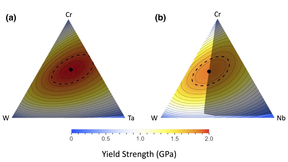
A materials science team, led by postdoctoral researcher Kate Elder, recently published a two-part series in npj Computational Materials. The research focuses on the computational discovery of ultra-strong, stable, and lightweight refractory metal-based multi-principal element alloys (MPEAs), which are compelling materials for high-temperature structural applications…
Professor Blair Brettmann from the Georgia Institute of Technology and her doctoral student Alexa Dobbs decided to spend a summer at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) to collaborate with the Lab’s materials science experts and learn more about LLNL’s experimental resources. During Brettmann’s faculty mini-sabbatical, she collaborated with researchers from LLNL…
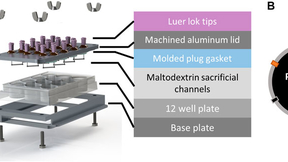
Colorectal cancer (CRC) — cancer of the colon or rectum — is the third-most common cancer in both men and women in the United States and the second-most common cause of cancer-related death in developed countries. Although surgery is highly successful for patients with a localized disease or disease confined to a narrow region (stages I–III), a total of 60% of CRC patients…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) computational scientists worked with experimental collaborators at Lawrence Berkeley and Sandia national laboratories to design metal amide-based composites capable of overcoming key kinetic limitations in their performance as hydrogen storage materials. Hydrogen possesses the highest energy density of any chemical fuel and can…
When SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft docked with the International Space Station (ISS) on March 16, it delivered several thousand pounds of supplies for the crew as well as new hardware. The hardware included the U.S. Space Force’s Space Test Program Houston 9 (STP-H9) platform, which houses a prototype telescope designed and built by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's…
Two scientists from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) are recipients of the Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Science Early Career Research Program award. Daniel Casey and Gauthier Deblonde are among 93 awardees receiving the recognition. Under the program, typical awards for DOE national laboratory staff are $500,000 per year for five years. “Supporting…
Machine learning techniques are increasingly being used in the sciences, as they can streamline work and improve efficiency. But these techniques are sometimes met with hesitation: When users don’t understand what’s going on behind the curtains, they may lack trust in the machine learning models. As these tools become more widespread, a team of researchers in Lawrence…
LLNL’s Materials Science Division (MSD) recently hosted an open house showcasing its lab facilities and redesigned workspaces that support the division’s expanding research scope. The event, led by Division Leader Manyalibo (Ibo) Matthews, featured tours of updated laboratory spaces. At each tour stop, MSD scientists provided a brief overview of the research that takes…
A new study provides surprising behavior of hydrogen bonding of water confined in carbon nanotubes. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists combined large-scale molecular dynamics simulations with machine learning interatomic potentials derived from first-principles calculations to examine the hydrogen bonding of water confined in carbon nanotubes (CNTs)…
A large portion of Greenland was an ice-free tundra landscape — perhaps covered by trees and roaming wooly mammoths — in the recent geologic past (about 416,000 years ago), according to a new study in the journal Science. The results shed light on the stability of the Greenland ice sheet, which was long assumed to have been frozen continuously over the last two and a half…
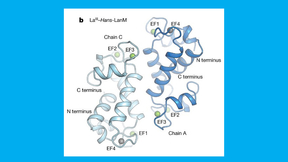
The irreplaceable roles of rare-earth (RE) elements in ubiquitous modern technologies ranging from permanent magnets to light-emitting diodes (LED) and phosphors have renewed interest in one of the grand challenges of separation science—efficient separation of lanthanides. However, the separation of these 15 elements is complicated due to their similar physicochemical…