Back
Though 2020 was dominated by events surrounding the COVID-19 pandemic — whether it was adapting to social distancing and the need to telecommute, safeguarding employees as they returned to conduct mission-essential work or engaging in COVID-related research — Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) managed an exceptional year in all facets of science and technology…
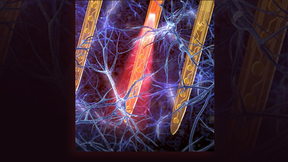
Combining hybrid polymer materials with microfabrication and 3D printing, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) has developed an ultra-compact, lightweight and minimally invasive optoelectronic neural implant that could be used for long-term studies of brain activity. The new implantable devices are built upon a new platform LLNL researchers are calling POEMS …
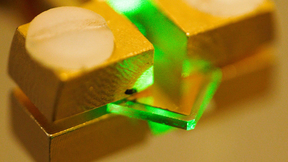
When it comes to the semiconductor industry, silicon has reigned as king in the electronics field, but it is coming to the end of its physical limits. To more effectively power the electrical grid, locomotives and even electric cars, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists are turning to diamond as an ultra-wide bandgap semiconductor. Diamond has been…
Texas A&M University’s Department of Nuclear Engineering on Dec. 10 announced it has honored Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) physicist Kelli Humbird with its 2020-21 Young Former Student award for her work at LLNL in combining machine learning with inertial confinement fusion (ICF) research. A design physicist at LLNL, Humbird graduated from Texas A&M…
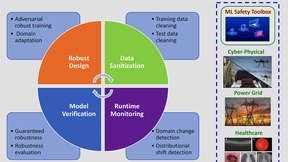
The 34th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) is featuring two papers advancing the reliability of deep learning for mission-critical applications at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). The most prestigious machine learning conference in the world, NeurIPS began virtually on Dec. 6. The first paper describes a framework for understanding…
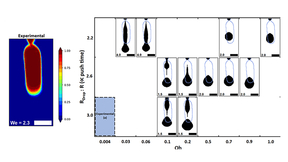
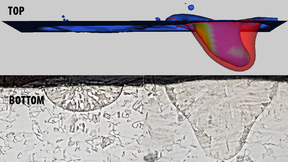
A team of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists has simulated the droplet ejection process in an emerging metal 3D printing technique called “Liquid Metal Jetting” (LMJ), a critical aspect to the continued advancement of liquid metal printing technologies. In the paper, the team describes the simulating of metal droplets during LMJ, a novel process in…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have taken a promising step in improving the reliability of laser-based metal 3D printing techniques by measuring the emission of electrons from the surface of stainless steel during laser processing. Researchers collected thermionic emission signals from 316L stainless steel under laser powder bed fusion (LPBF)…
Fifty-seven researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) were among the top 2 percent of the most cited researchers worldwide throughout their careers, according to research on metascience by Stanford University. Metascience is the "study of studies" using scientific methods. Stanford University professor John Loannidis worked alongside U.S.-based Kevin…
Alkaline water electrolysis has been touted as a path to establish a hydrogen economy by converting intermittent renewable energies into clean hydrogen-based chemical energy. However, current technology has achieved only low current densities and voltage efficiencies. To make electrolysis more resourceful, a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team partnered with…
A team of current and former Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and IBM scientists won the annual “Test of Time” award at the 2020 Supercomputing Conference on Nov. 19 for a paper outlining LLNL’s Blue Gene/L supercomputer. Published by the Supercomputing Conference in 2002, the paper was the first peer-reviewed overview article to disclose details of Blue Gene…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have used multi-material 3D printing to create tailored gradient refractive index glass optics that could make for better military specialized eyewear and virtual reality goggles. The new technique could achieve a variety of conventional and unconventional optical functions in a flat glass component (with no surface…
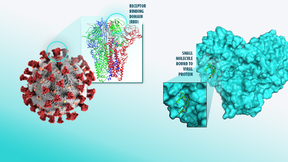
A machine learning model developed by a team of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists to aid in COVID-19 drug discovery efforts is a finalist for the Gordon Bell Special Prize for High Performance Computing-Based COVID-19 Research. Using Sierra, the world’s third fastest supercomputer, LLNL scientists created a more accurate and efficient generative…
The Department of Energy (DOE) today announced two rounds of awards for the High Performance Computing for Energy Innovation Program (HPC4EI), including five projects at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). HPC4EI connects industry with the computational resources and expertise of the DOE national laboratories to solve challenges in manufacturing, accelerate…
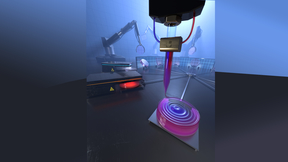
Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have adapted a new class of materials for their groundbreaking volumetric 3D printing method that produces objects nearly instantly, greatly expanding the range of material properties achievable with the technique. The class of materials adapted for volumetric 3D printing are called thiol-ene resins, and they can…
Brain aneurysms affect about one in every 50 Americans and can lead to serious medical emergencies, including stroke, brain damage and death if they burst. Existing treatment options are limited and often invasive, and surgical outcomes can vary widely from person to person. But medical practitioners may be able to improve existing treatment methods and develop new…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists have paired 3D-printed, living human brain vasculature with advanced computational flow simulations to better understand tumor cell attachment to blood vessels, the first step in secondary tumor formation during cancer metastasis. The unique approach, developed with outside collaborators, lays the foundation for…
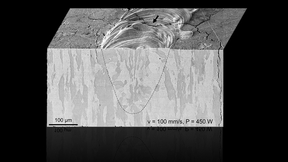
Boasting the highest melting and boiling points of all known elements, tungsten has become a popular choice for applications involving extreme temperatures, including lightbulb filaments, arc welding, radiation shielding and, more recently, as plasma-facing material in fusion reactors such as the ITER Tokamak. However, tungsten’s inherent brittleness, and the microcracking…
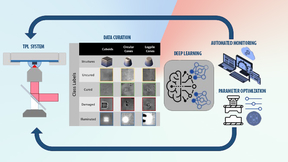
Two-photon lithography (TPL) — a widely used 3D nanoprinting technique that uses laser light to create 3D objects — has shown promise in research applications but has yet to achieve widespread industry acceptance due to limitations on large-scale part production and time-intensive setup. Capable of printing nanoscale features at a very high resolution, TPL uses a laser…
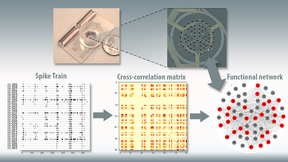
For the past several years, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and engineers have made significant progress in development of a three-dimensional “brain-on-a-chip” device capable of recording neural activity of human brain cell cultures grown outside the body. Now, LLNL researchers have a way to computationally model the activity and structures of…
Following weeks of prototyping, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is partnering with private industry to mass-produce a simple mechanical ventilator developed for COVID-19 patients that has been authorized for emergency use by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). LLNL and medical device startup company BioMedInnovations (BMI) have reached an agreement…