Back
This week, President Biden signed into law the bipartisan bill known as the CHIPS and Science Act (CSC ACT). The bill aims to strengthen U.S. competition by encouraging U.S. companies to manufacture semiconductors and by revitalizing “America’s scientific research and technological leadership." Under Title V: Broadening Participation in Science of the bill, the White House…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists have created a new adjoint waveform tomography model that more accurately simulates earthquake and explosion ground motions. The paper, published in the Journal of Geophysical Research, was selected for an Editor’s Highlight. Seismic tomography is a method to estimate the inaccessible three-dimensional (3D) seismic…
Last month, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), a partnership with the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency, revealed unprecedented and detailed views of the universe, with the release of its first full-color images and spectroscopic data. The cosmic objects that Webb targeted for these first observations were released July 12 and are available on the…
After decades of inertial confinement fusion research, a yield of more than 1.3 megajoules (MJ) was achieved at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL’s) National Ignition Facility (NIF) for the first time on Aug. 8, 2021, putting researchers at the threshold of fusion gain and achieving scientific ignition. On the one-year anniversary of this historic achievement,…
The graphite-diamond phase transition is of particular interest for fundamental reasons and a wide range of applications. On very fast compression time scales, material kinetics hinder the transition from graphite to the equilibrium cubic diamond crystal structure that we commonly know as diamond. Shock wave compression of graphite typically requires pressures above 50 GPa…
Metal 3D printing is used to produce components for many commercial applications, particularly in the transportation sector, where printing methods such as laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF) can produce super-strong and ultralight complex-shaped components that cannot be manufactured with conventional techniques. But while laser-based methods enable the manufacturing of…
As of 2020, 102.9 million smart meters — devices that record and communicate electric consumption, voltage and current to consumers and grid operators — have been installed in the United States. As the number of smart meters and the demand for energy is expected to increase by 50 percent by 2050, so will the amount of data those smart meters produce. While energy standards…
Scientists at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) Energetic Materials Center and Purdue University Materials Engineering Department used simulations performed on the LLNL supercomputer Quartz to uncover a general mechanism that accelerates chemistry in detonating explosives critical to managing the nation’s nuclear stockpile. Their research is featured in the…
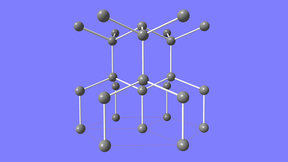
Various types of iron oxide (FeO) are typically distinguished by the number of iron and oxygen atoms coordinated with one another. However, specific iron and oxygen coordination is also an important factor to consider, as a molecule’s various phases can exhibit vastly different material properties. In recent years, epsilon-phase iron oxide (ε-Fe2O3), a rare polymorph of…
Additive manufacturing is essential to the production of advanced materials, providing a straightforward approach to rapid prototyping and manufacturing. Direct ink writing (DIW), a subset of additive manufacturing, offers a versatile route to ink extrusion—a processing method where a viscous ink is forced through a nozzle but behaves like a solid when printed on a…
Gareth Trubl and researchers from Sandia National Laboratories have created a new computer tool called Tiger2 that scans DNA and looks for genomic islands—sections that look different than the surrounding DNA. Genomic islands are important for understanding life, infection, evolution, and more. These sections typically house antibiotic resistant and toxin producing genes…
Soil is the largest terrestrial reservoir of organic carbon and is central for climate change mitigation and adaptation. Mineral-organic associations play a critical role in soil carbon preservation, but the global capacity for storage in this form has never been quantified. New research from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and an international team of…
A visit to Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) last summer by a university professor led to a unique internship opportunity for an undergraduate student this summer: helping LLNL scientists fabricate higher-performing carbon aerogel structures for electrodes and other energy-storage applications. In 2021, Professor Anthony Santamaria from Western New England (WNE…
A team of researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and the University of Michigan has found that the rate of cooling in reactions dramatically affects the type of uranium molecules that form. The team’s experimental work, conducted over about a year-and-a-half starting in October 2020, attempts to help understand what uranium compounds might form in…
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) team will be among the first researchers to perform work on the world’s first exascale supercomputer — Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Frontier — when they use the system to model cancer-causing protein mutations. Led by Harsh Bhatia, a computer scientist in the Center for Applied Scientific Computing (CASC) at LLNL, the team…
For the first time, scientists have shown that glaciers in the tropical Andes mountains have been in sync with polar ice extent in Antarctica and the Arctic for nearly a million years. New research by an international team, including Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientist Christine Y. Chen, records glacier movement in the Southern Hemisphere that dates…
Deep below the Black Hills of South Dakota in the Sanford Underground Research Facility (SURF), an innovative and uniquely sensitive dark matter detector — the LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) experiment, led by Lawrence Berkeley National Lab (Berkeley Lab) — has passed a check-out phase of startup operations and delivered its first results. In a paper posted online today on the experiment…
The next generations of lithium-ion batteries require higher energy and power densities at a lower cost. Current battery manufacturing, based on slurry casting and coating, is struggling to further improve these key metrics. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is partnering with Ampcera Inc. to develop solvent-free Laser Powder Bed Fusion (L-PBF) additive…
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists recently obtained high-precision thermodynamic data on warm dense nitrogen at extreme conditions that could lead to a better understanding of the interiors of celestial objects like white dwarfs and exoplanets. The team, which includes researchers from the University of California, Berkeley and the University of…
Two Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists are recipients of the prestigious 2021 E.O. Lawrence Award that recognizes mid-career U.S. scientists and engineers for exceptional scientific, technical and engineering achievements related to the broad missions of the Department of Energy (DOE) and its programs. Jennifer Pett-Ridge was recognized for her…