Researchers identify pressure effects on nanomaterials
 (Download Image)
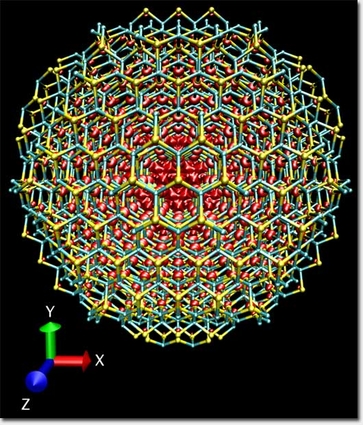
Image by Sebastien Hamel/LLNL Fluorescence from CdSe quantum dot solids in environments varying from stable to highly unstable show that small deviations from uniform stress distribution greatly affect the electronic properties. The blue represents cadmium, the yellow represents selenium and the red represents a cloud of electrons in their excited state.
(Download Image)
Image by Sebastien Hamel/LLNL Fluorescence from CdSe quantum dot solids in environments varying from stable to highly unstable show that small deviations from uniform stress distribution greatly affect the electronic properties. The blue represents cadmium, the yellow represents selenium and the red represents a cloud of electrons in their excited state.
Transistors, lasers and solar-energy conversion devices may be easier to manipulate because of recent research by Laboratory scientists.
The researchers defined the role high pressure plays in precisely tuning the fundamental properties of nanomaterials and, in particular, nanoparticle assemblies that are important for device applications.
The team, made up of Laboratory scientists Christian Grant, Jonathan Crowhurst, Sebastien Hamel, Natalia Zaitseva and former LLNL researcher Andrew Williamson (now at Physic Ventures), subjected quantum dot solids (in this case, assemblies of cadmium selenide, or CdSe, nanocrystals) to very high static pressures on the order of 70,000 atmospheres and studied in-situ their response using a laser-based luminescence technique. A quantum dot is a semiconductor whose electrons are confined in all three spatial dimensions.
"We closely compared our results with theoretical calculations," Grant said. "These results were completely consistent with our experimental observations."
However, when they applied nonuniform pressure, the results were quite different. It led to large shifts in the energy associated with the very strong fluorescence of CdSe. CdSe, it was found, is extremely sensitive to the local stress state.
The typical length of quantum dots, which are anywhere in size from one to several hundred nanometers, have chemical and physical properties that are substantially different from those of their bulk and molecular counterparts. (A nanometer is one-billionth of a meter.)
Quantum dots can be close-packed into quantum dot solids (QDSs). These nanomaterials can yield insight not only into particle-particle coupling, but also tell a story of the evolution of their electronic properties from individual dots to the collective solid.
The Livermore team measured QDSs in several different pressure media, including a liquid and various solid or glassy but still fairly soft media. In addition, they compressed the material directly. Depending on the medium, they observed a steady increase in energy as a function of pressure (uniform pressure case) or after an initial increase, a flattening or even decrease in energy (non-uniform pressure case).
"High pressure provides insight into the fundamental properties of nanoparticles, which can be drastically different from the corresponding bulk material," Grant said.
For example, the structural phase transition that occurs in bulk CdSe occurs at much lower pressures than in the case of the QDSs.
The research appears in the June issue of the journal Small .




